Piezo buzzers are basic components with versatility to emit tones, beeps, and even melodies. In this codelab, learn how to set up a piezo buzzer with your Raspberry Pi, and start making sound with just a few lines of code. Whether you're building a fun alert system or adding sound effects to a DIY project, you can integrate a piezo buzzer into your Viam project quickly using a prebuilt module.

What You'll Build
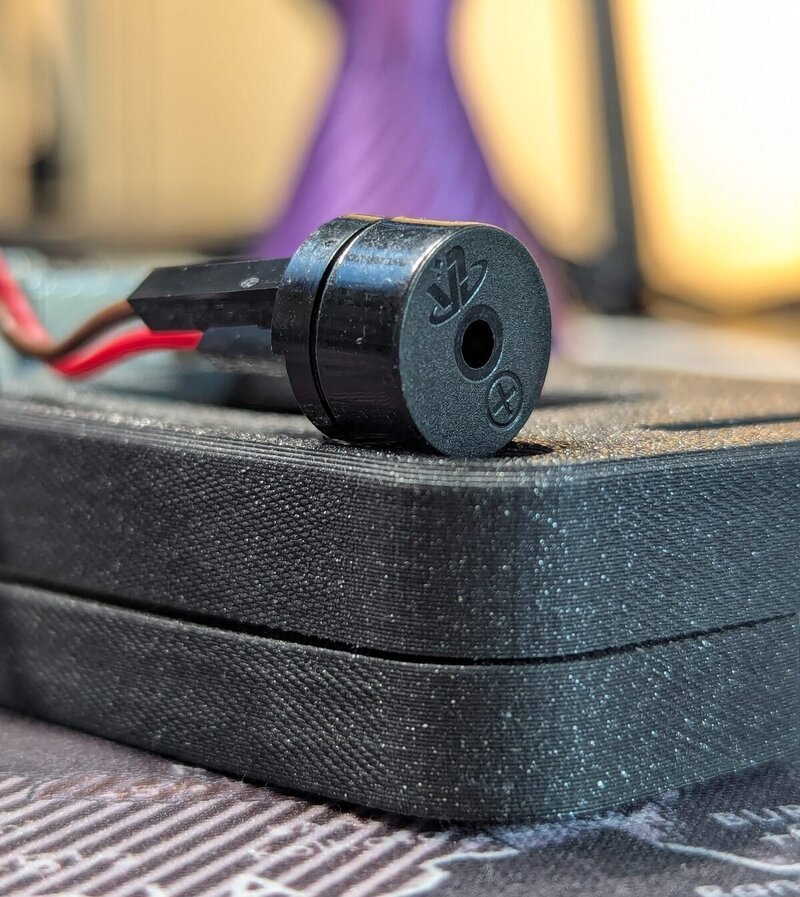
- A passive piezo buzzer that can emit a tone and a melody.

Prerequisites
- A computer with MacOS, Windows, or Linux to flash your Raspberry Pi and configure the device's components using the Viam app
- Hardware and supplies requirements
- 1 - Raspberry Pi 4
- 1 - microSD card to use with your Pi
- 1 - power supply for your Pi
- 1 - passive piezo buzzer
- 2 - jumper wires
What You'll Need
- All the hardware components listed in prerequisites.
- Sign up for a free Viam account, and then sign in to the Viam app
What You'll Learn
- How to configure and test a device's components using Viam
- How to use modules from the Viam registry
- How to use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the sound of a passive piezo
Watch the Video
See a demonstration sounding the piezo buzzer in this video.
The Raspberry Pi boots from a USB flash drive (or microSD card). You need to install Raspberry Pi OS on a USB flash drive that you will use with your Pi. For more details about alternative methods of setting up your Raspberry Pi, refer to the Viam docs.
Install Raspberry Pi OS
- Connect the USB flash drive (or microSD card) to your computer.
- Download the Raspberry Pi Imager and launch it.
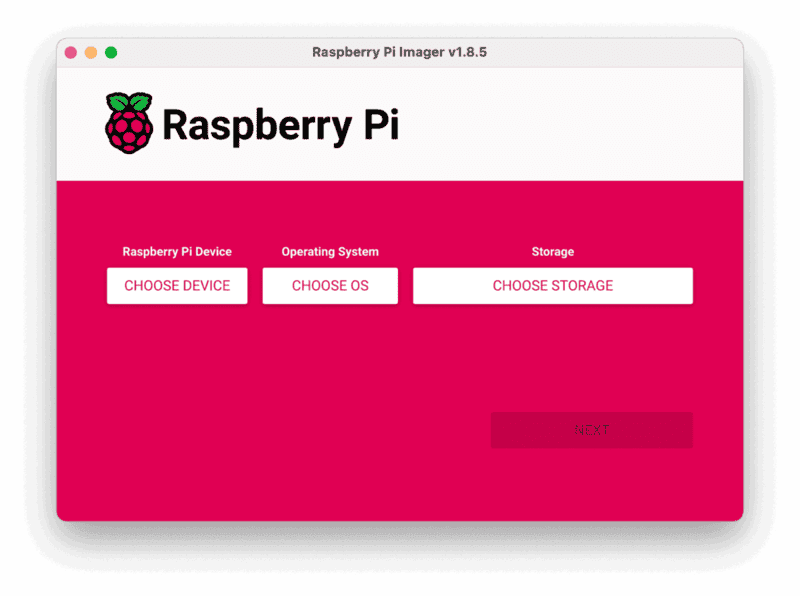
- Click CHOOSE DEVICE. Select your model of Pi, which is Raspberry Pi 4.
- Click CHOOSE OS. Select Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit) from the menu.
- Click CHOOSE STORAGE. From the list of devices, select the USB flash drive you intend to use in your Raspberry Pi.
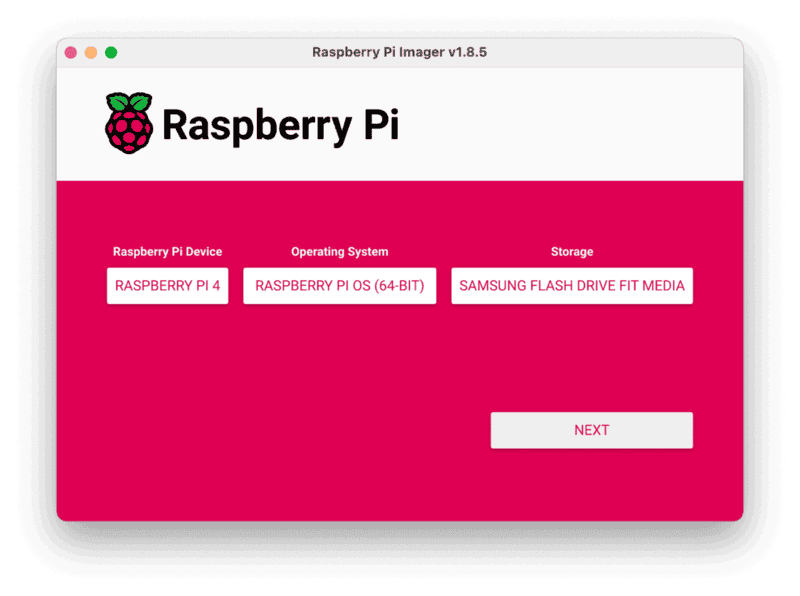
- Configure your Raspberry Pi for remote access. Click Next. When prompted to apply OS customization settings, select EDIT SETTINGS.
- Check Set hostname and enter the name you would like to access the Pi by in that field, for example,
test. - Select the checkbox for Set username and password and set a username (for example, your first name) that you will use to log into the Pi. If you skip this step, the default username will be
pi(not recommended for security reasons). And specify a password. - Connect your Pi to Wi-Fi so that you can run
viam-serverwirelessly. Check Configure wireless LAN and enter your wireless network credentials. SSID (short for Service Set Identifier) is your Wi-Fi network name, and password is the network password. Change the sectionWireless LAN countryto where your router is currently being operated.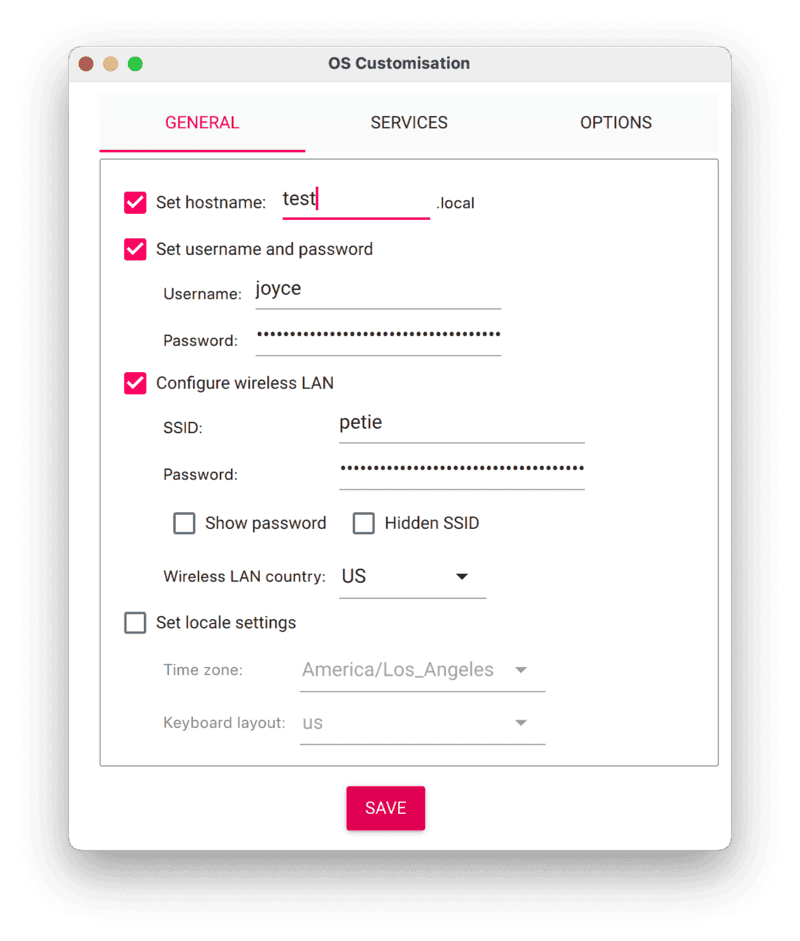
- Select the SERVICES tab, check Enable SSH, and select Use password authentication.
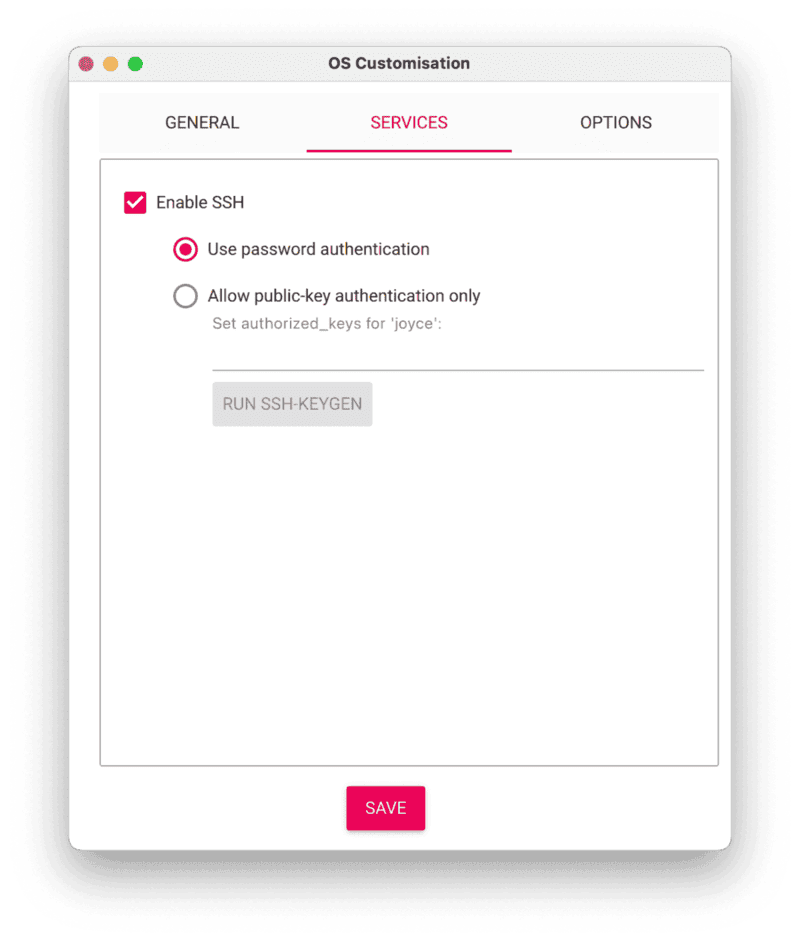
- Save your updates, and confirm
YESto apply OS customization settings. ConfirmYESto erase data on the USB flash drive. You may also be prompted by your operating system to enter an administrator password. After granting permissions to the Imager, it will begin writing and then verifying the Linux installation to the USB flash drive. - Remove the USB flash drive from your computer when the installation is complete.
Connect with SSH
- Place the USB flash drive into your Raspberry Pi and boot the Pi by plugging it in to an outlet. A red LED will turn on to indicate that the Pi is connected to power.
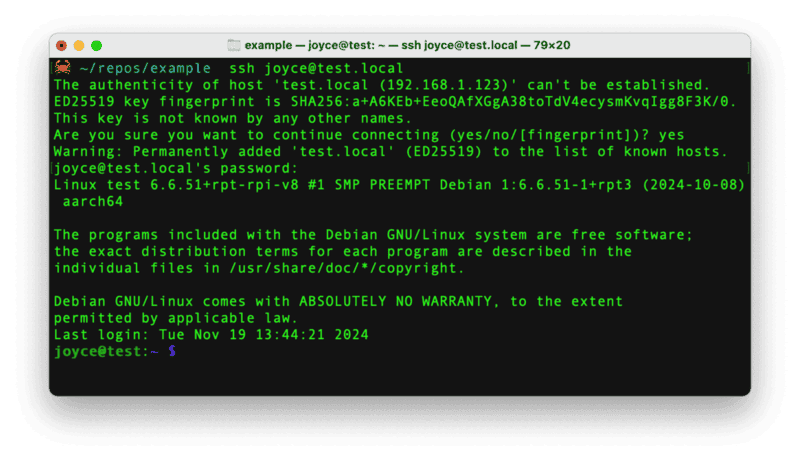
- Once the Pi is started, connect to it with SSH. From a command line terminal window, enter the following command. The text in <> should be replaced (including the < and > symbols themselves) with the user and hostname you configured when you set up your Pi.
ssh <USERNAME>@<HOSTNAME>.local - If you are prompted "Are you sure you want to continue connecting?", type "yes" and hit enter. Then, enter the password for your username. You should be greeted by a login message and a command prompt.
- Update your Raspberry Pi to ensure all the latest packages are installed
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Add your piezo buzzer
- Connect the piezo buzzer: The passive piezo buzzer can be controlled via a GPIO pin on the Raspberry Pi. Refer to the following wiring diagram to connect the Raspberry Pi to the piezo buzzer.
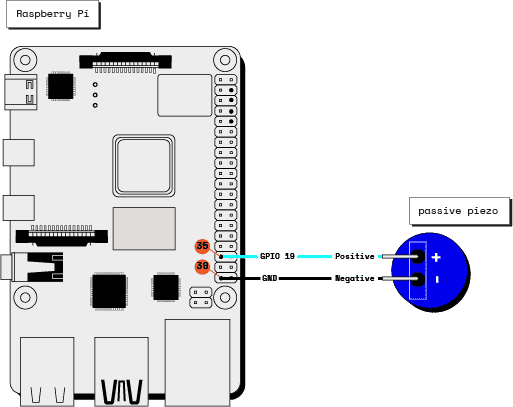
- Pin 35 (GPIO 19) to Positive
- Pin 39 (GND) to Negative
Now that we have physically connected our hardware components, let's configure the software in the next section.
Configure your machine
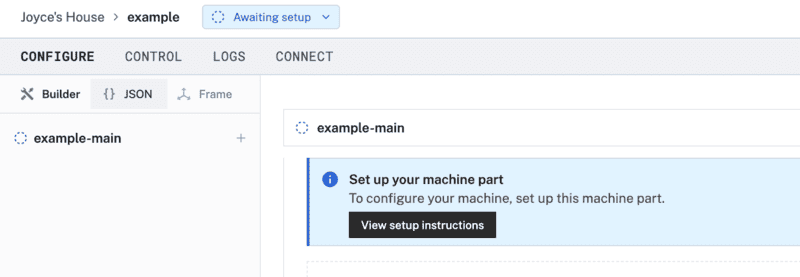
- In the Viam app under the LOCATIONS tab, create a machine by typing in a name and clicking Add machine.

- Click View setup instructions.
- To install
viam-serveron the Raspberry Pi device that you want to use to communicate with and control your webcam, select theLinux / Aarch64platform for the Raspberry Pi, and leave your installation method asviam-agent.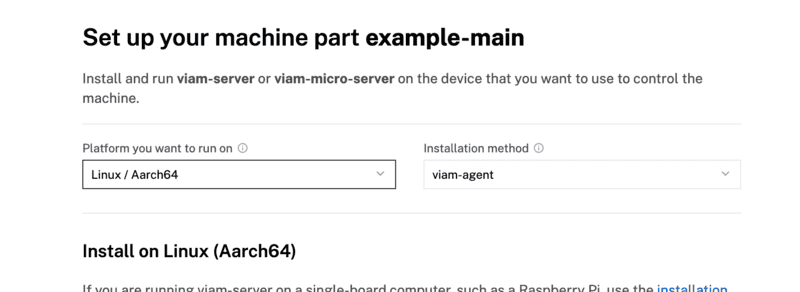
- Use the
viam-agentto download and installviam-serveron your Raspberry Pi. Follow the instructions to run the command provided in the setup instructions from the SSH prompt of your Raspberry Pi.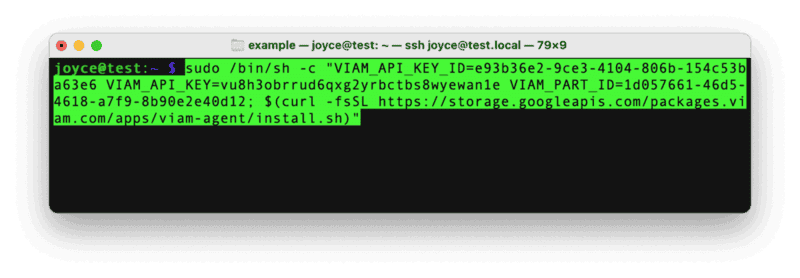
- The setup page will indicate when the machine is successfully connected.

Configure your Raspberry Pi board
To access the GPIO pins, let's add our Raspberry Pi board to our machine in the Viam app.
- In the Viam app, find the CONFIGURE tab.
- Click the + icon in the left-hand menu and select Component.
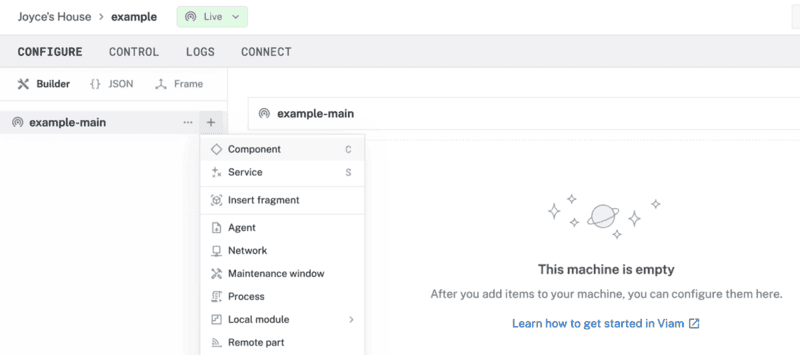
- Select
board, and find theraspberry-pi:rpi4module. This adds the module for working with the Raspberry Pi 4's GPIO pins. Leave the default nameboard-1for now. - Notice adding this module adds the board hardware component called
board-1. The collapsible card on the right corresponds to the part listed in the left sidebar.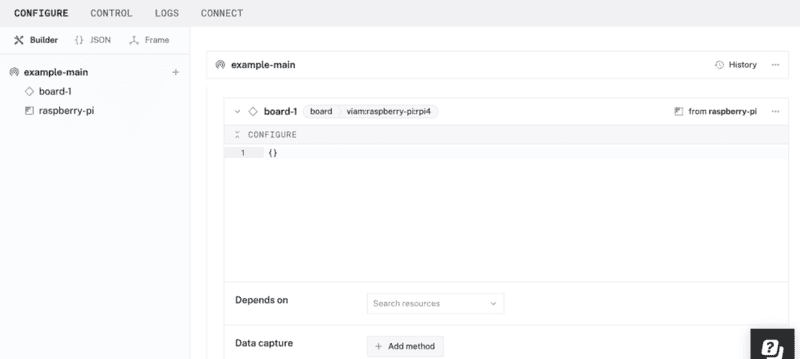
- Click Save in the top right to save and apply your configuration changes.
- Expand the TEST section of the panel to experiment with writing to physical pin
35. For example, try setting aHighsignal, along with70% duty cycle and1200Hz frequency.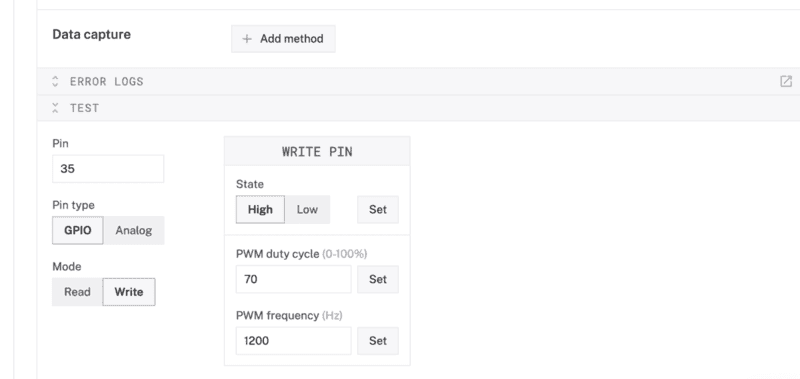
- Set the signal to
Lowto turn off the buzzer.
You can manually and programmatically use the GPIO pins of the board component to send PWM signals to control your buzzer. However, to streamline the following steps, let's use a prebuilt module from the Viam registry in the next section.
Configure your piezo buzzer
- In the Viam app under the CONFIGURE tab, click the + icon in the left-hand menu and select Component.
- Select
generic, and find thebuzzer:piezomodule. This adds the module for controlling your buzzer. Name the componentpiezo.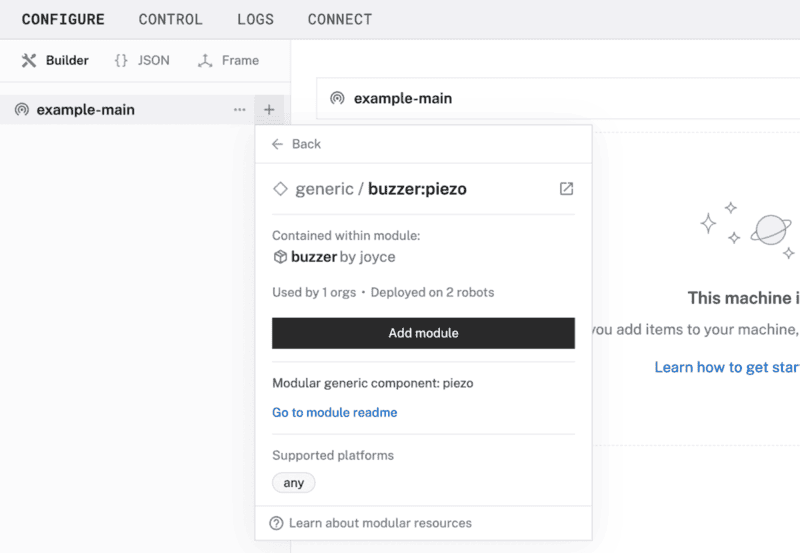
- In the new
piezopanel, configure your component by adding the following attributes in the CONFIGURE field. This tells your piezo component to use a specific pin (physical pin 35) on a specific board (calledboard-1in the Viam app).{ "piezo_pin": "35", "board": "board-1" } - Select your board
board-1from the Depends on field.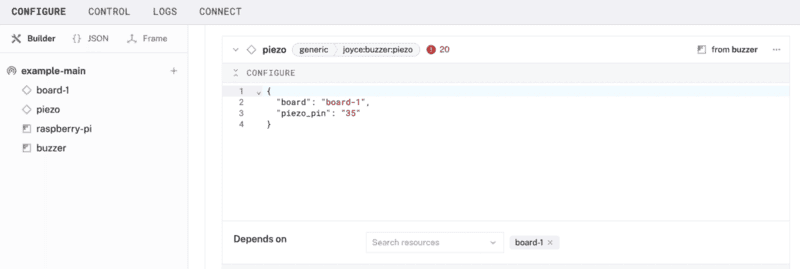
- Click Save to apply your configuration changes. This may take a moment.
- Since we are using a generic component, let's test it out under the CONTROL tab. Find your
piezocomponent on this page. Expand the DO COMMAND field, input the following code, and hit Execute.{ "sound_buzzer": { "frequency": 1200, "duration": 1.5, "duty_cycle": 0.7 } }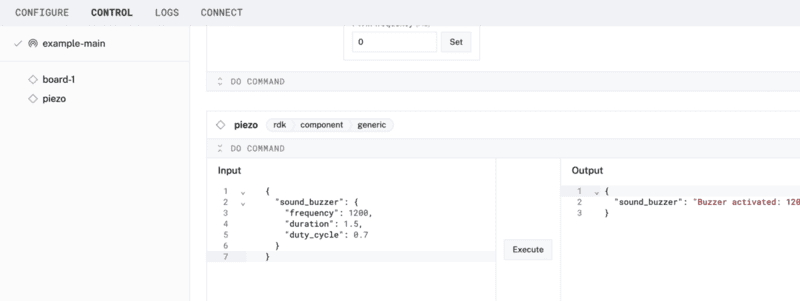 You are executing a
You are executing a DoCommandon a generic component that has been predefined to accept parameters such asfrequency,duration, andduty_cycle. - Experiment with different values in those fields to see what happens when you execute the command again. If you have extra time, try sending the following Do command.
{ "play_harry_potter": {} }
What is the primary purpose for using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control a passive piezo buzzer?
What you learned
- How to configure and test a device's components using Viam
- How to use modules from the Viam registry
- How to use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the sound of the buzzer
Building advanced scenarios with Viam and piezo buzzers
At this point, you have configured and tested your machine and piezo buzzer to make sound, but nothing is happening automatically. You can create automatic processes that trigger actions when certain conditions are met, such as in the following examples.
- When a person is detected, as described in this workshop for People detection alert with Computer Vision
- When air quality values reach a certain threshold, as described in this codelab to Automate air filtration with air quality sensors
- When a QR code is detected, as described in this codelab to Use a QR code scanner

You can 3-D print a case for the Raspberry Pi that allows access to your GPIO pins for expanding your project (like this one here). You can also design and 3-D print a custom mount to hold your buzzer in place, or 3-D print a megaphone (like this one here) to amplify the buzzer volume.
In addition to the project ideas mentioned above, consider other ways to continue your journey with Viam.
- Browse other modules in the Viam registry similar to the prebuilt module for the buzzer.
- Learn how to create your own module with custom functionality for the piezo buzzer or other components and services.
Real-world applications and projects for piezo buzzers
Piezo buzzers are small, but mighty components used in industries requiring audible feedback, alerts, or tone generation. Their applications include:
- Alarms and Alerts: Piezo buzzers create auditory signals in security systems, smoke detectors, and medical devices to notify users of critical events or malfunctions.
- Interactive Robotics: Robots use piezo buzzers to provide audio feedback to signal a task is completed or to prompt user interaction.
- Home Automation: Smart home devices and other consumer electronics utilize piezo buzzers for notifications, such as doorbell chimes, appliance alerts, or system warnings.
- Gaming and Toys: Toys and games use piezo buzzers for sound effects and melodies, enhancing the interactive user experience.