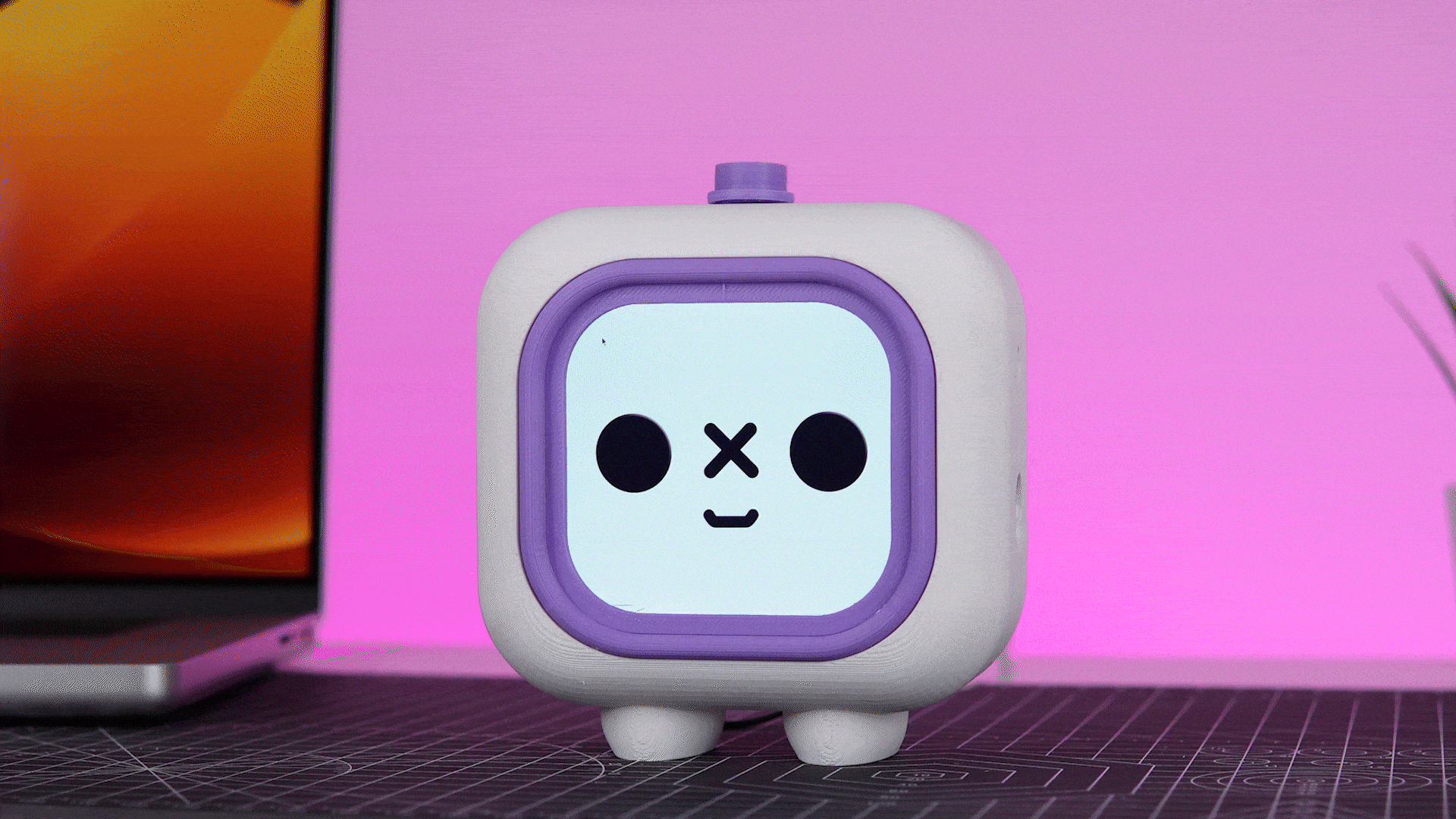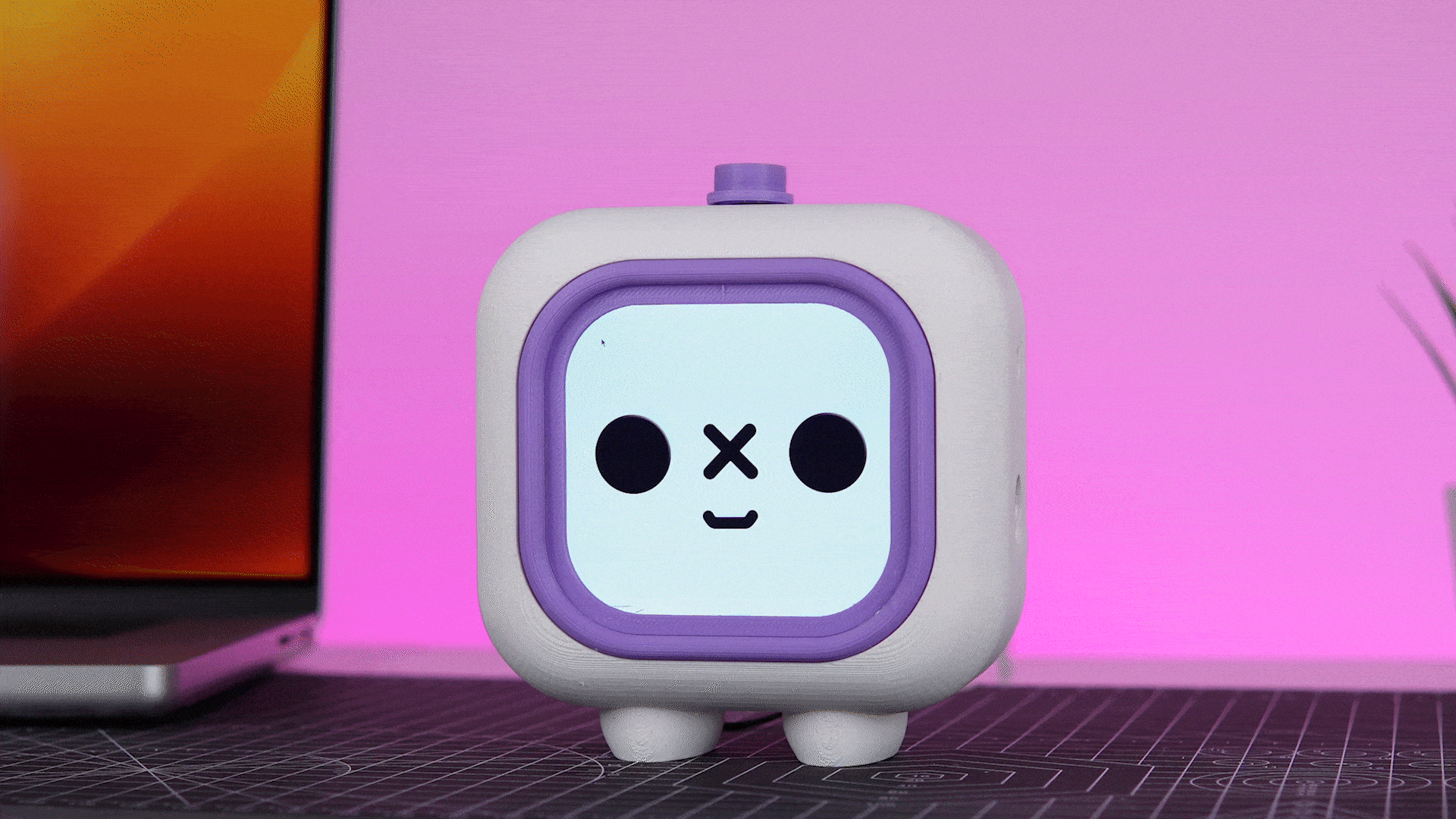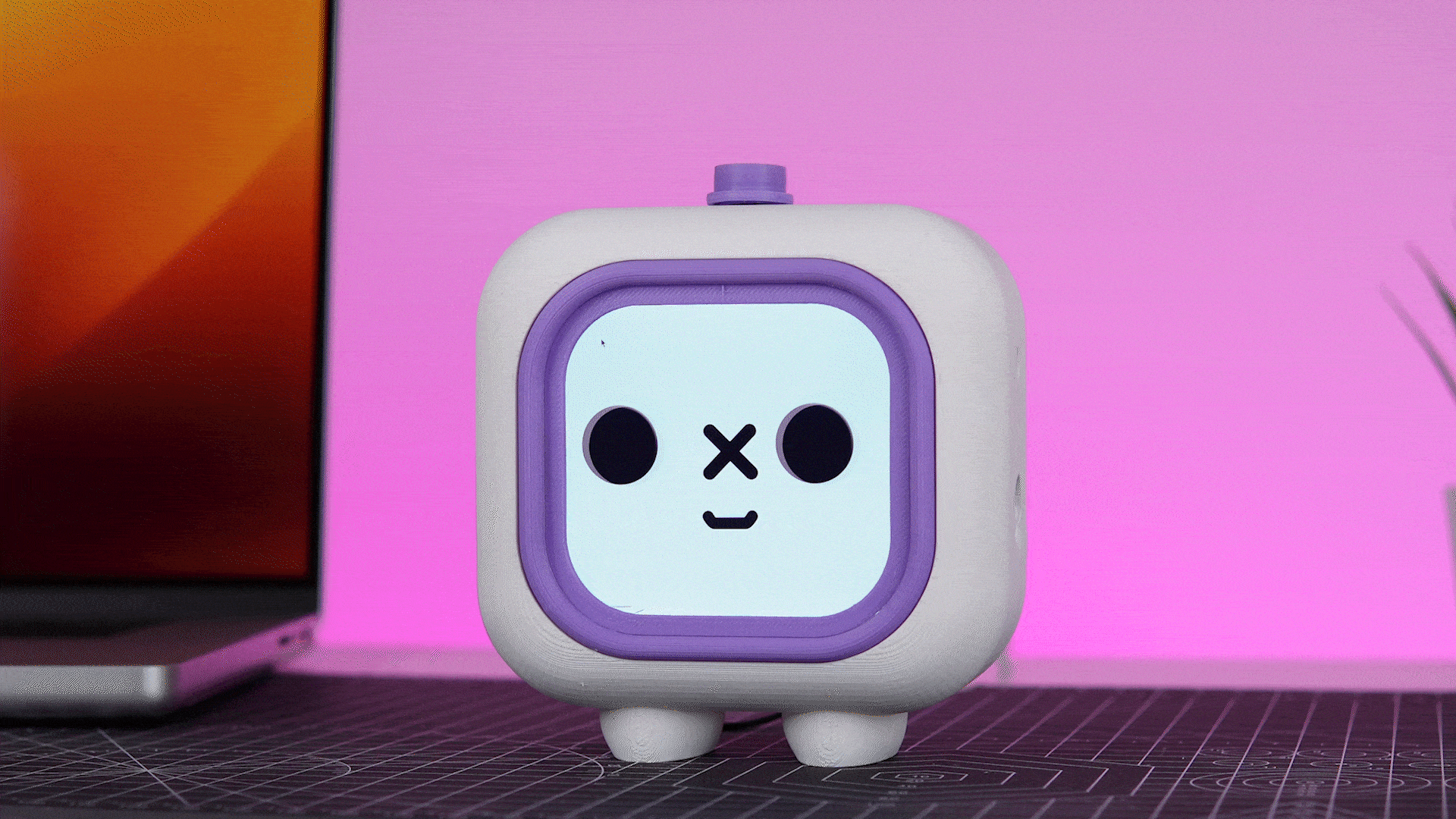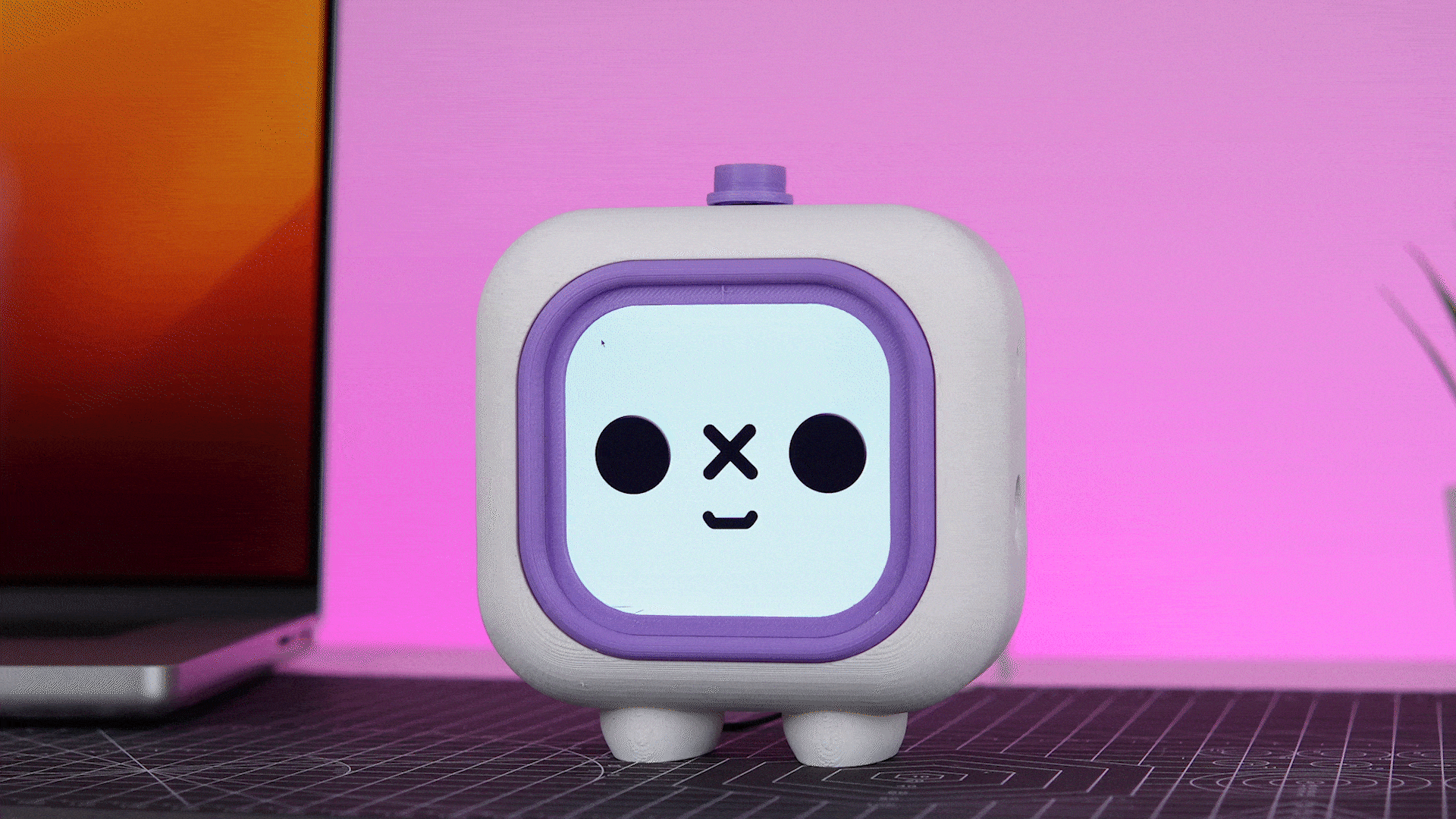
In today's fast-paced world, staying productive while maintaining focus can be challenging. Meet the Pomodoro Bot, your desktop companion designed to revolutionize the way you work. Built using Viam's versatile robotics platform and powered by the Raspberry Pi, this innovative tool goes beyond the traditional Pomodoro timer by integrating modern sensors and smart alerts to create a seamless productivity experience.
Features include:
- Pomodoro Timer: Master the Pomodoro Technique to enhance your focus and efficiency.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Ensure your workspace is optimal for productivity by tracking CO₂, VOC levels and AQI.
- Light Quality Alerts: Optimize lighting conditions for reduced eye strain and better concentration.
- Meeting Reminders: Stay on top of your schedule with proactive alerts for upcoming meetings.
With a sleek design and a focus on intelligent functionality, the Pomodoro Bot is more than just a timer; it's your dedicated partner in productivity. Whether you're working from home or at the office, this bot ensures you stay productive, healthy, and on schedule.

Prerequisites
- Sign up for a free Viam account, and then sign in to the Viam app
- Hardware and Supplies
- 1 - Raspberry Pi 5
- 1 - microSD card to use with your Pi
- 1 - Raspberry Pi Official Power Supply
- 1 - 4inch HDMI Capacitive Touch IPS LCD Display
- 1 - Fermion: ENS160 Air Quality Sensor
- 1 - TEMT6000: An Ambient Light Sensor
- 1 - Push Button Module
- 1 - USB Type C Breakout Board - Female
- 1 - USB Type C Breakout Board - Male
- 1 - Silicone Wire
- Software Requirements
Watch The Video
Let's start by seeing our Pomodoro Bot in action!
The Raspberry Pi boots from a USB flash drive (or microSD card). You need to install Raspberry Pi OS on a USB flash drive that you will use with your Pi. For more details about alternative methods of setting up your Raspberry Pi, refer to the Viam docs.
Install Raspberry Pi OS
- Connect the USB flash drive (or microSD card) to your computer.
- Download the Raspberry Pi Imager and launch it.
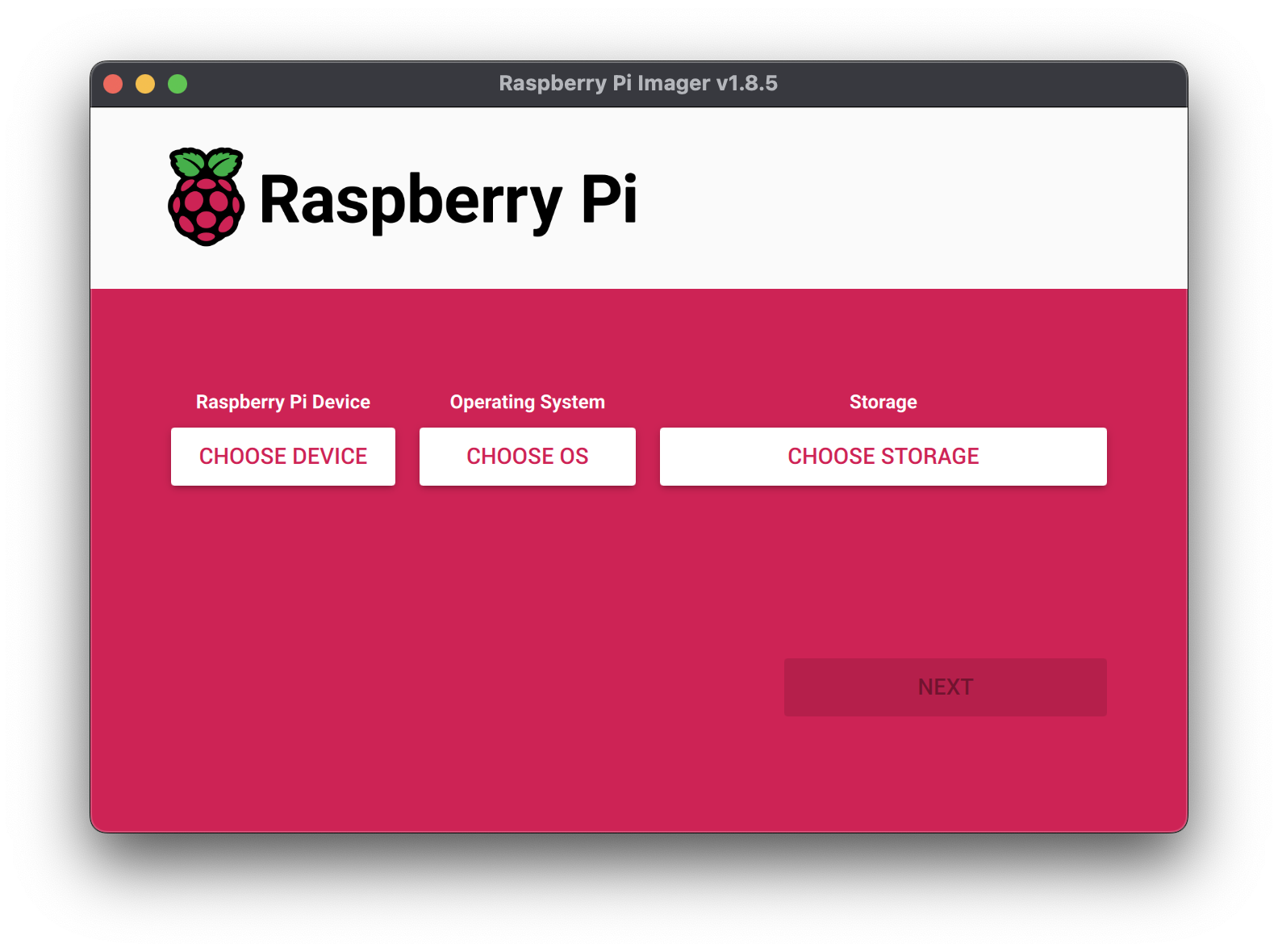
- Click CHOOSE DEVICE. Select your model of Pi, which is Raspberry Pi 5.
- Click CHOOSE OS. Select Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit) from the menu.
- Click CHOOSE STORAGE. From the list of devices, select the USB flash drive you intend to use in your Raspberry Pi.
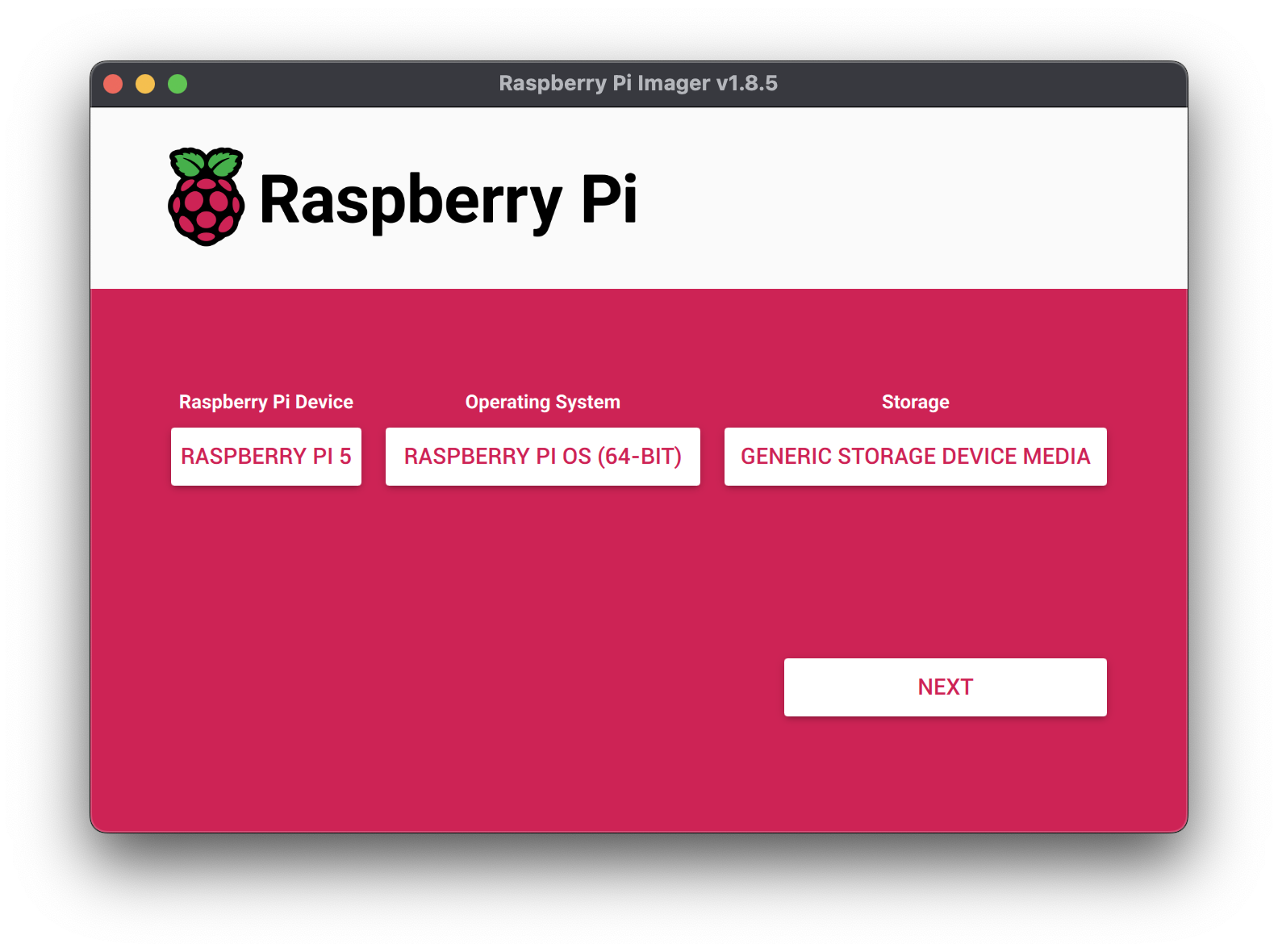
- Configure your Raspberry Pi for remote access. Click Next. When prompted to apply OS customization settings, select EDIT SETTINGS.
- Check Set hostname and enter the name you would like to access the Pi by in that field, for example,
raspberrypi. - Select the checkbox for Set username and password and set a username (for example, your first name) that you will use to log into the Pi. If you skip this step, the default username will be
pi(not recommended for security reasons). And specify a password. - Connect your Pi to Wi-Fi so that you can run
viam-serverwirelessly. Check Configure wireless LAN and enter your wireless network credentials. SSID (short for Service Set Identifier) is your Wi-Fi network name, and password is the network password. Change the sectionWireless LAN countryto where your router is currently being operated.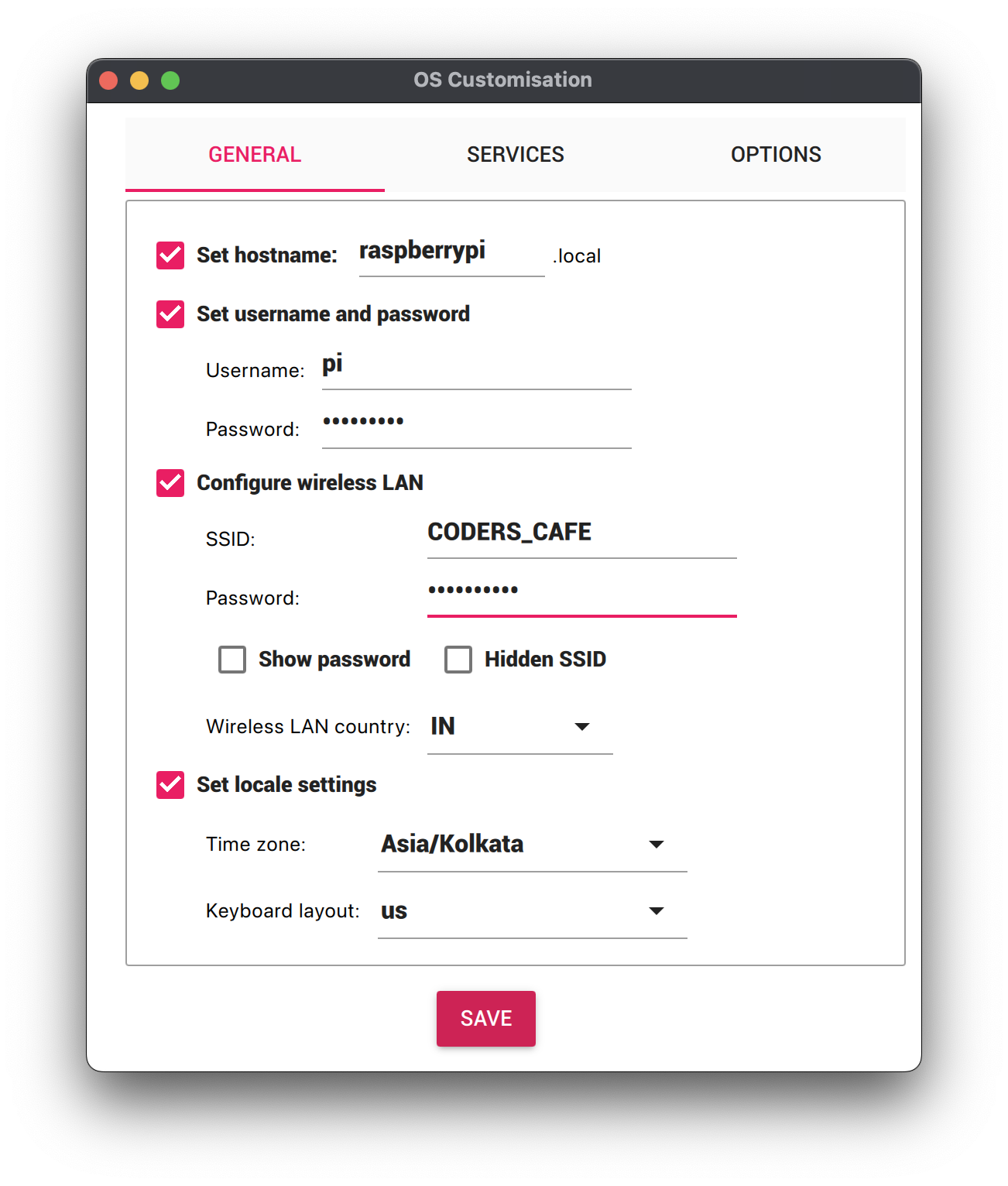
- Select the SERVICES tab, check Enable SSH, and select Use password authentication.
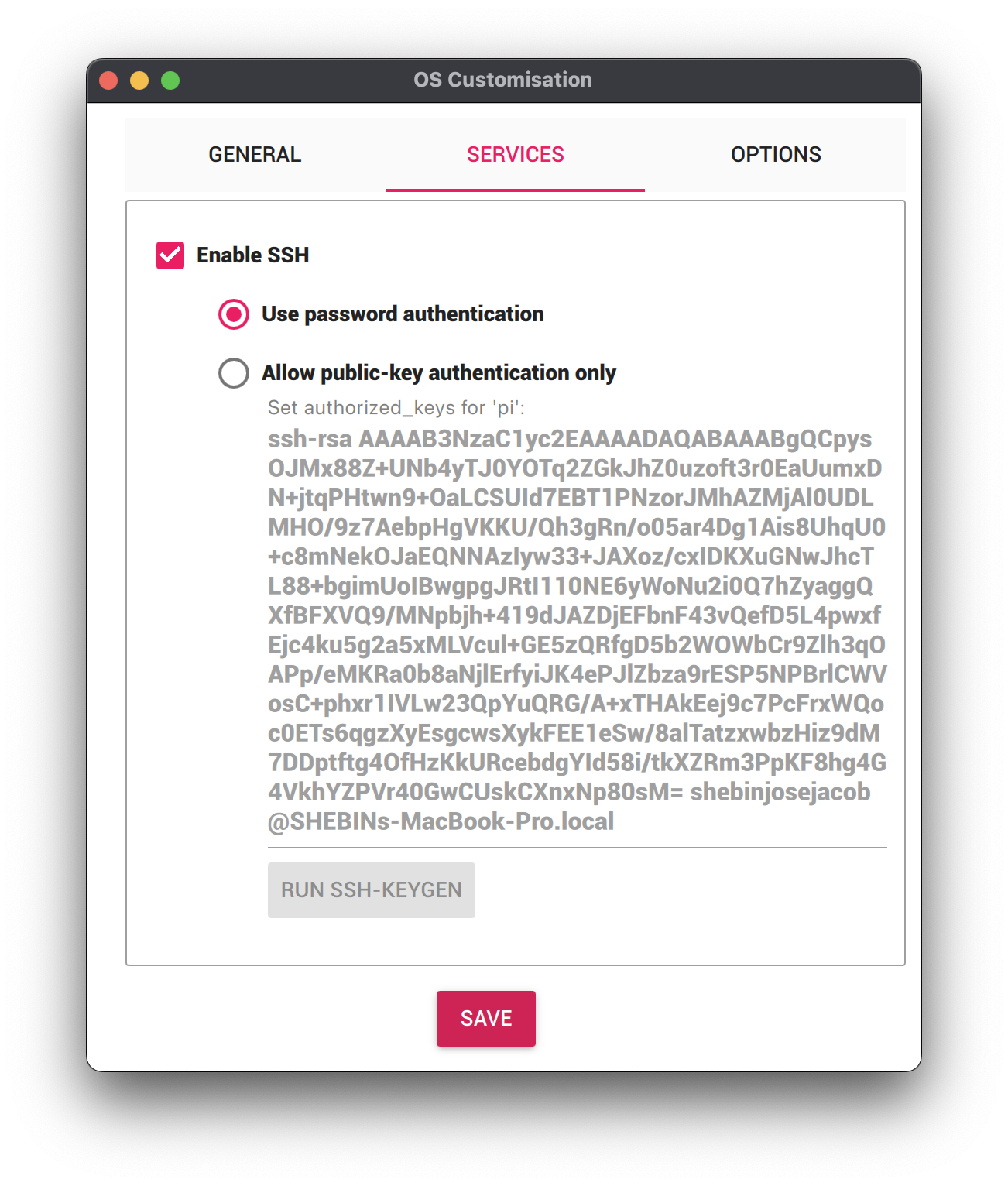
- Save your updates, and confirm
YESto apply OS customization settings. ConfirmYESto erase data on the USB flash drive. You may also be prompted by your operating system to enter an administrator password. After granting permissions to the Imager, it will begin writing and then verifying the Linux installation to the USB flash drive. - Remove the USB flash drive from your computer when the installation is complete.
Connect with SSH
- Place the USB flash drive into your Raspberry Pi and boot the Pi by plugging it in to an outlet. A red LED will turn on to indicate that the Pi is connected to power.
- Once the Pi is started, connect to it with SSH. From a command line terminal window, enter the following command. The text in <> should be replaced (including the < and > symbols themselves) with the user and hostname you configured when you set up your Pi.
ssh <USERNAME>@<HOSTNAME>.local - If you are prompted "Are you sure you want to continue connecting?", type "yes" and hit enter. Then, enter the password for your username. You should be greeted by a login message and a command prompt.
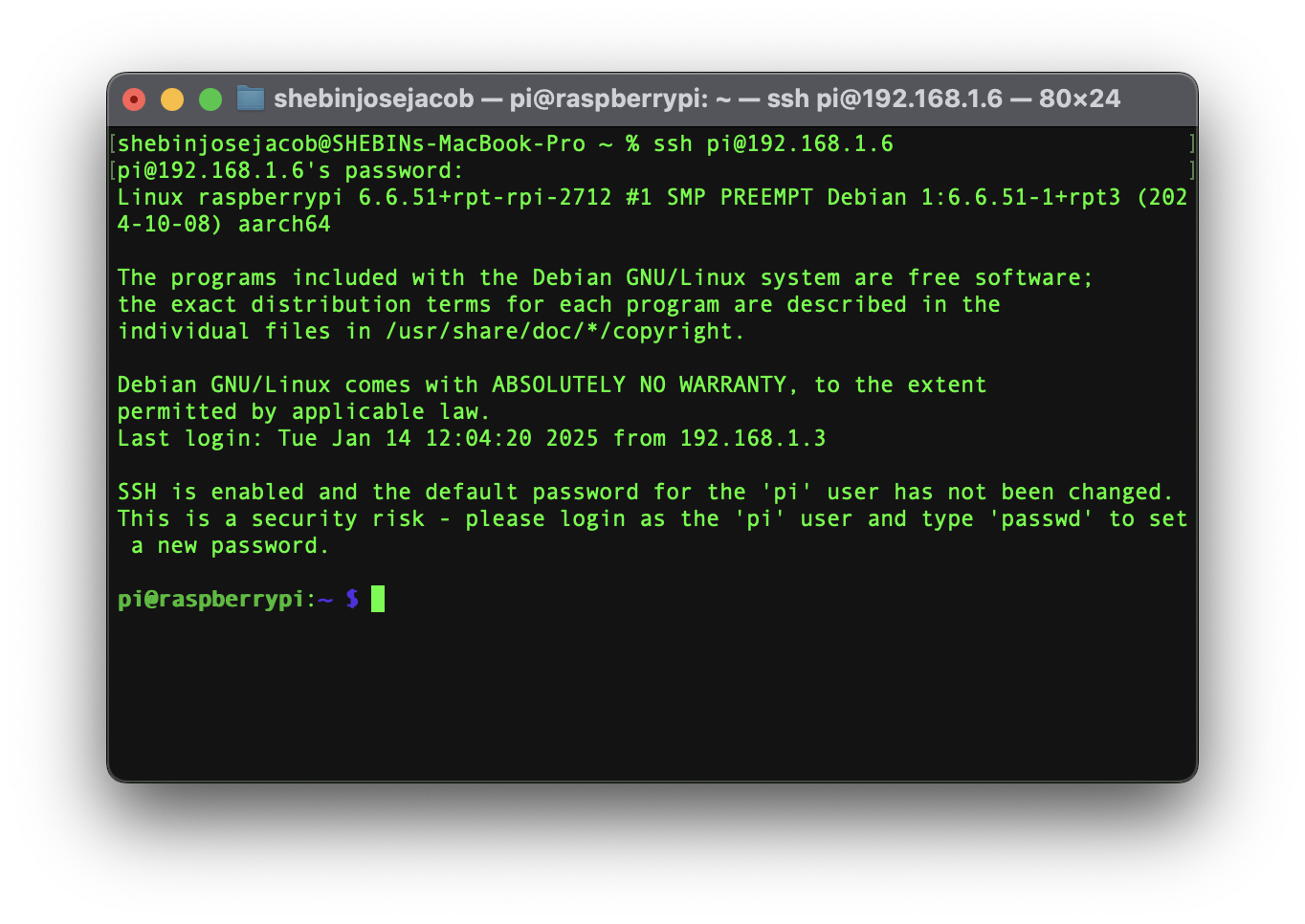
- Update your Raspberry Pi to ensure all the latest packages are installed
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Enable communication protocols
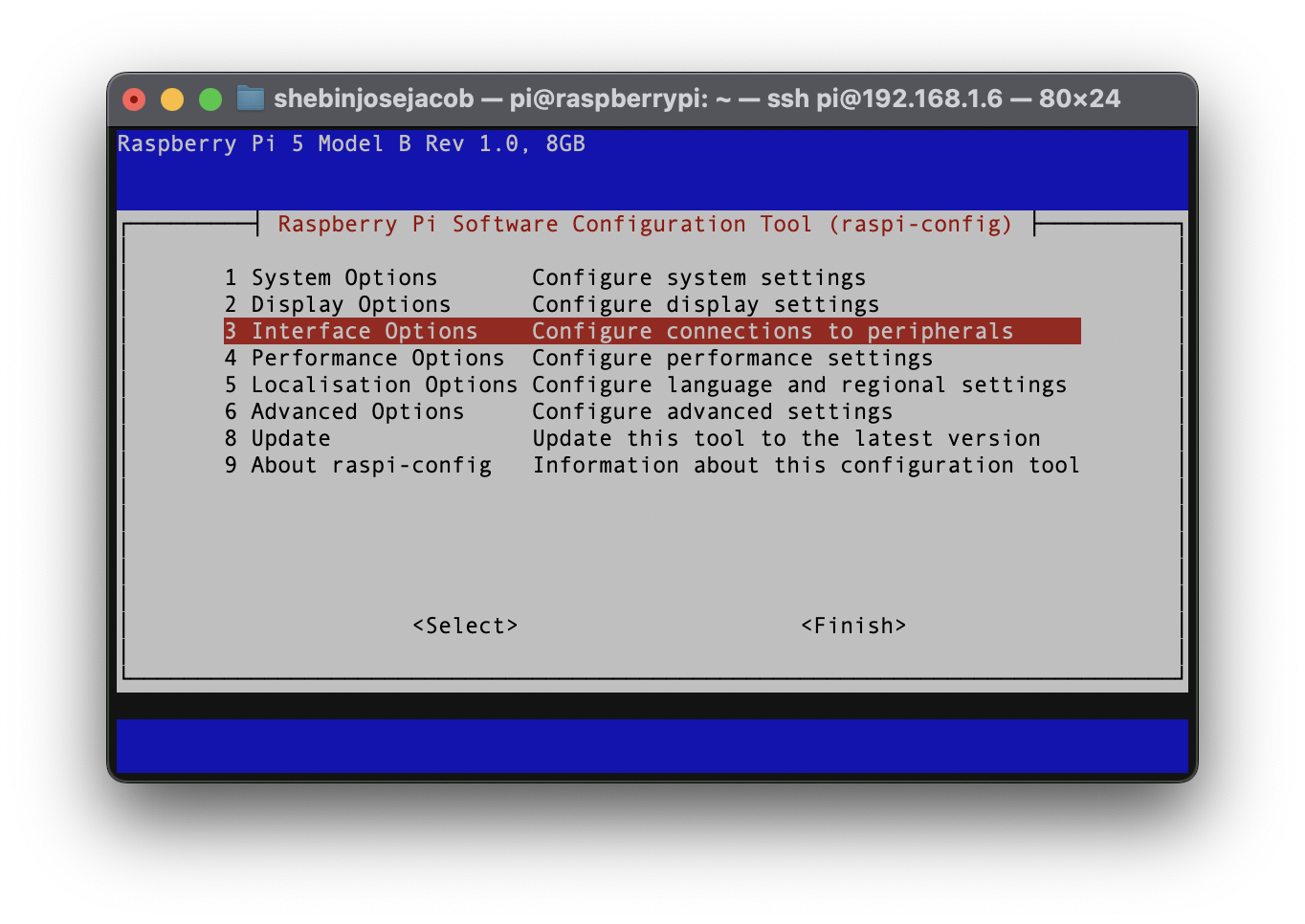
- Launch the Pi configuration tool by running the following command
sudo raspi-config - Use your keyboard to select "Interface Options", and press return.
- Enable the relevant protocols to support our hardware. Since you are using a sensor that communicates over the I2C, enable I2C.
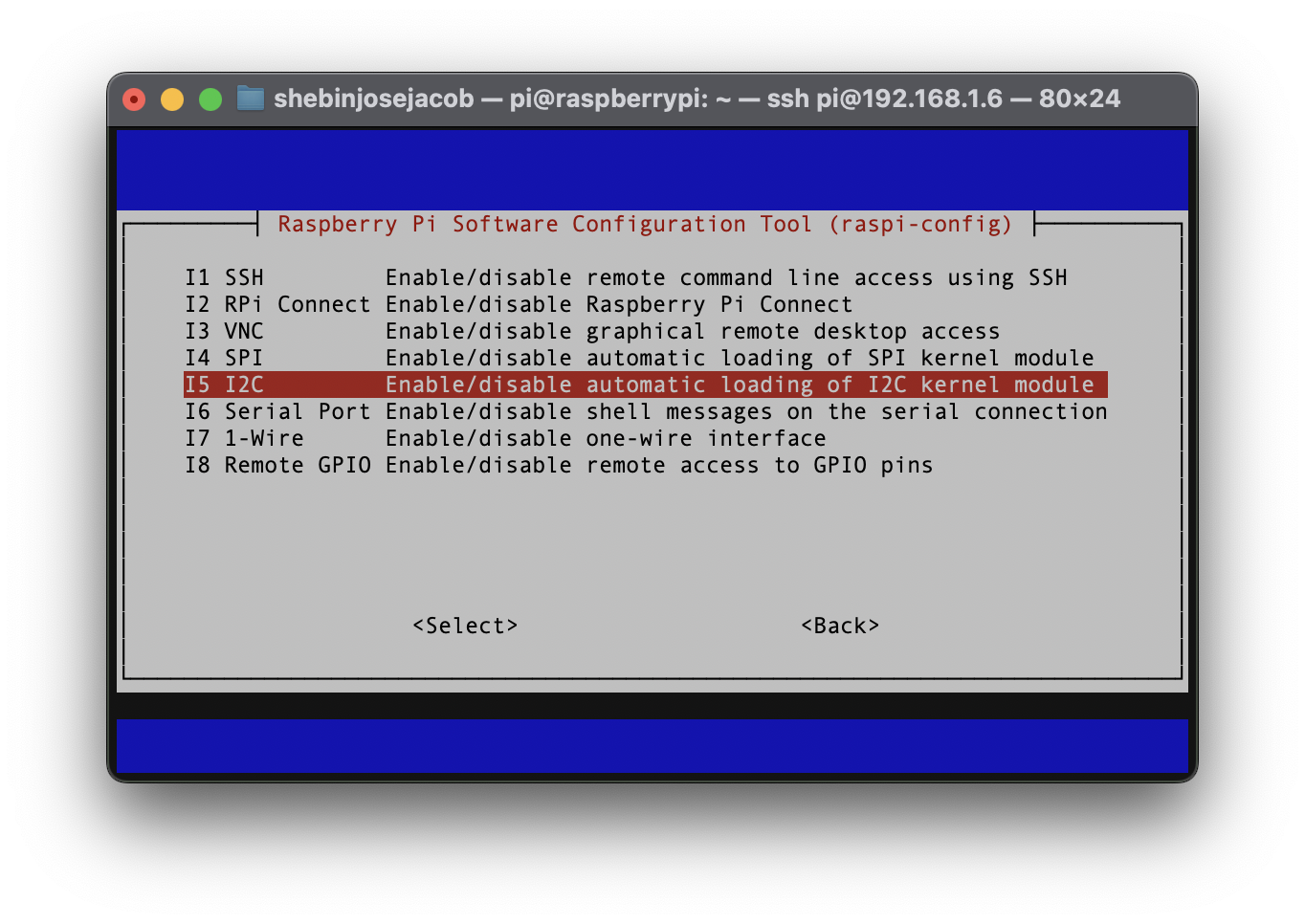
- Confirm the options to enable I2C interface. And reboot the Pi when you're finished.
Create Your Machine
- In the Viam app under the LOCATIONS tab, create a machine by typing in a name and clicking Add machine.
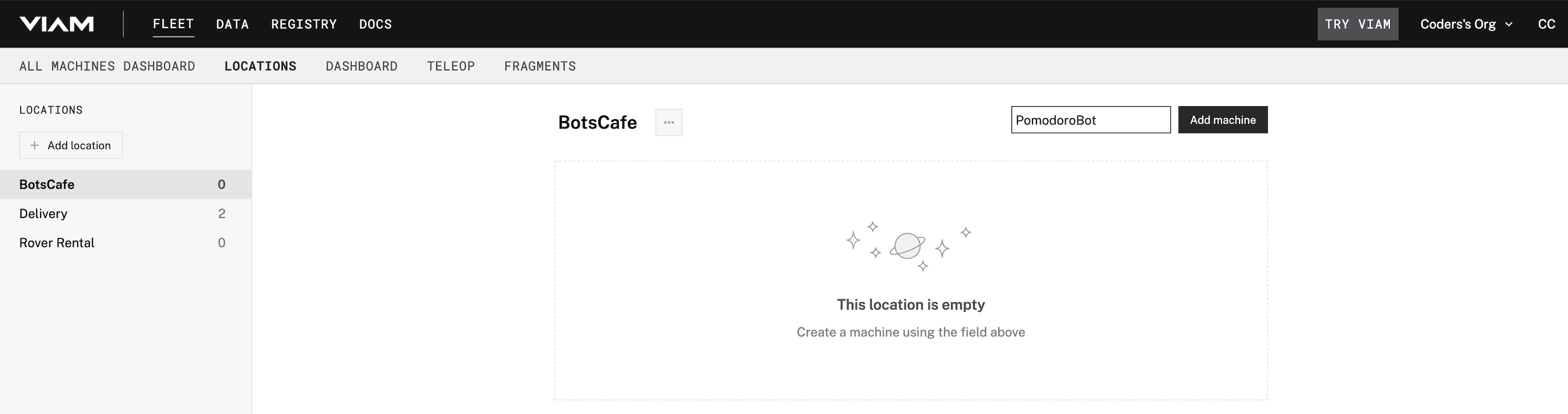
- Click View setup instructions.
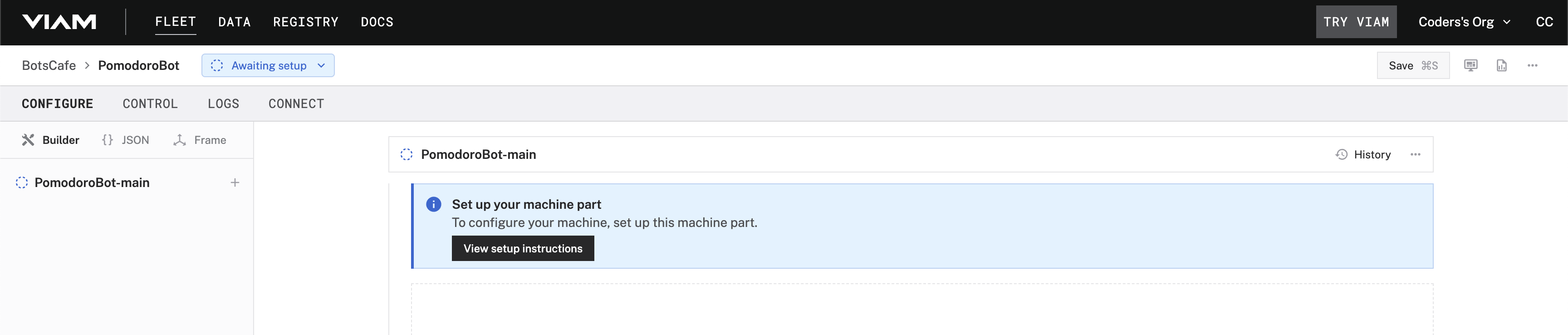
- Install
viam-serveron the Raspberry Pi device that you want to use to communicate with and control your Pomodoro Bot. Select theLinux / Aarch64platform for the Raspberry Pi, and leave your installation method asviam-agent.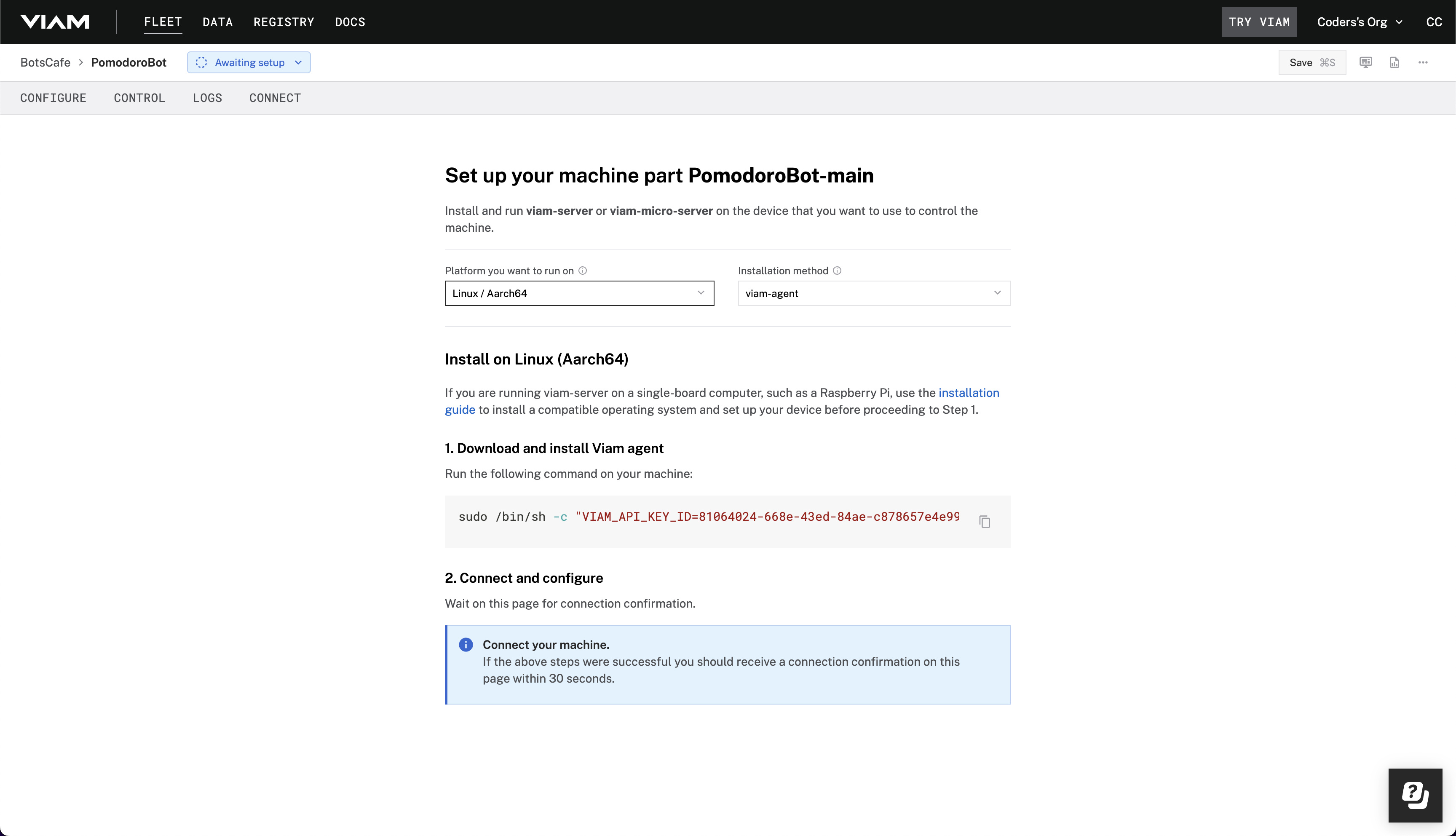
- Use the
viam-agentto download and installviam-serveron your Raspberry Pi. Follow the instructions to run the command provided in the setup instructions from the SSH prompt of your Raspberry Pi.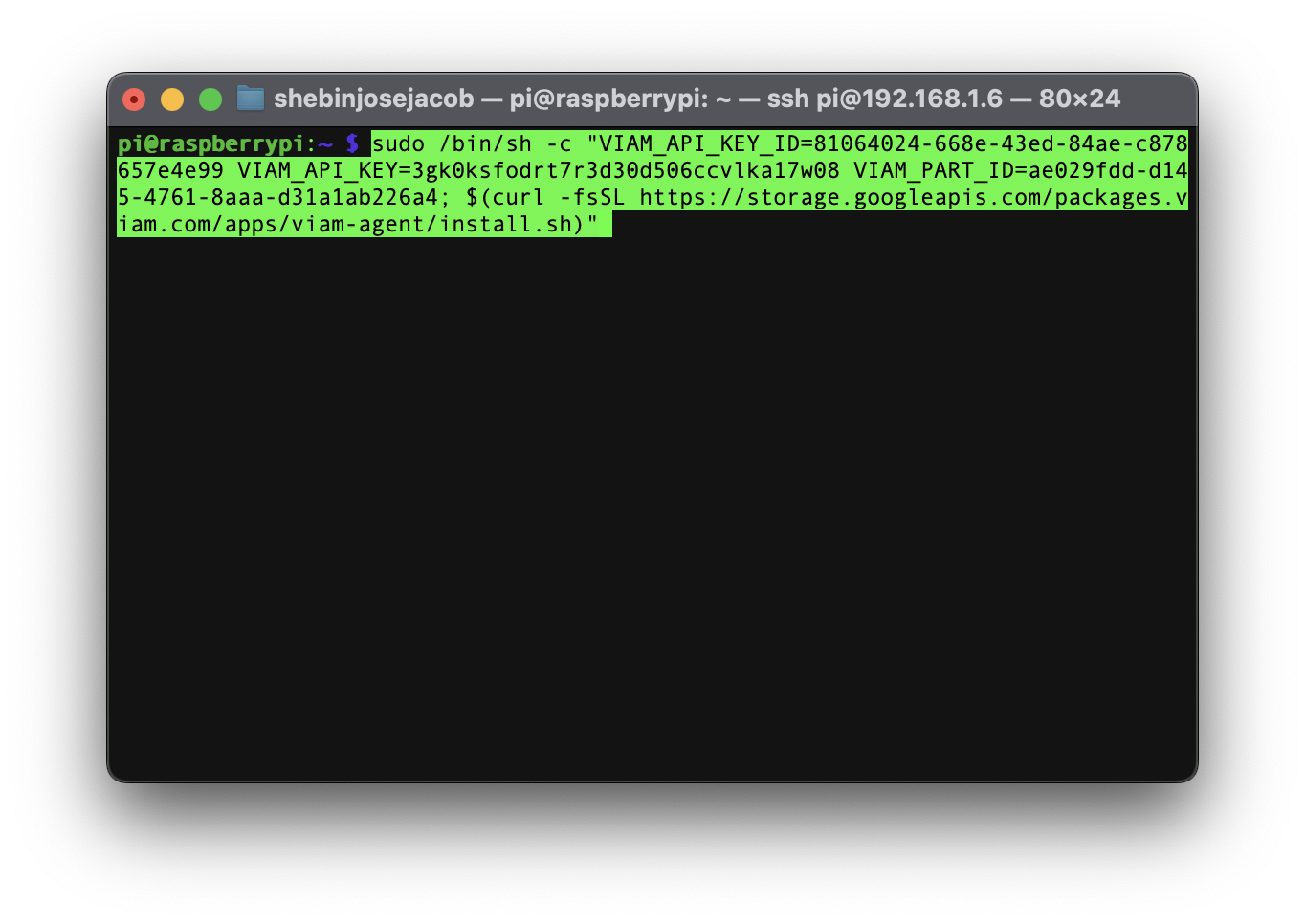 The setup page will indicate when the machine is successfully connected.
The setup page will indicate when the machine is successfully connected.
Add your Raspberry Pi
- In the Viam app, find the CONFIGURE tab. It's time to configure your hardware.
- Click the + icon in the left-hand menu and select Component.
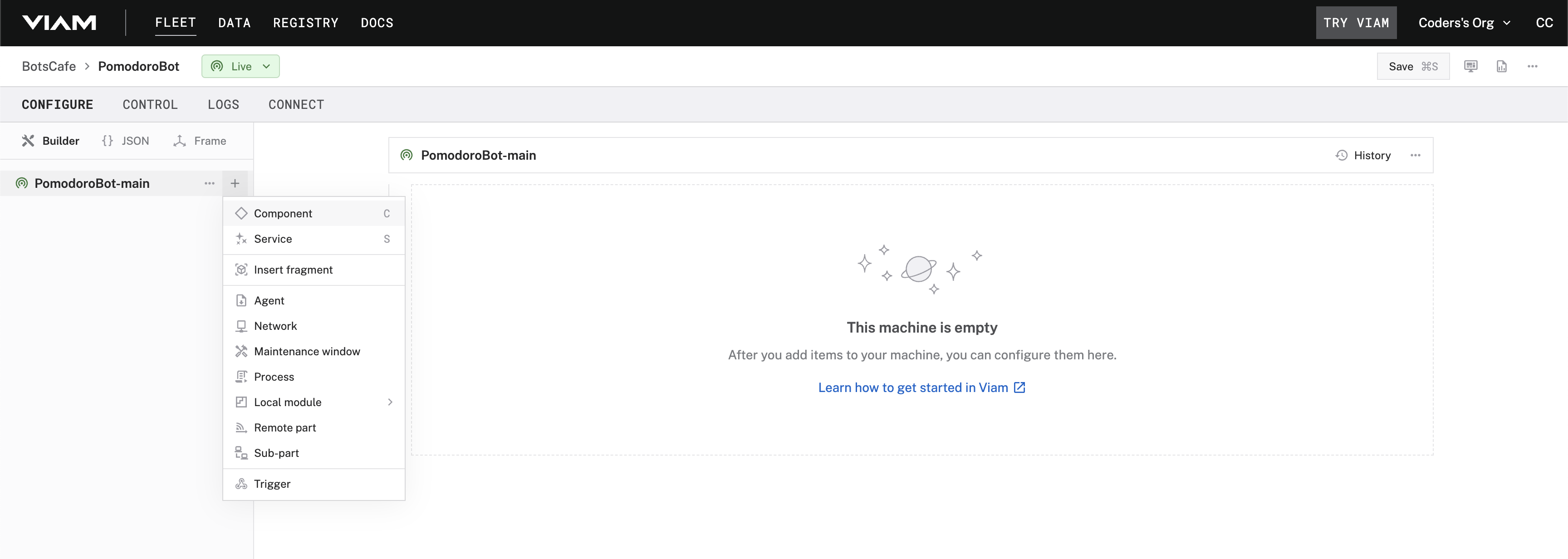
- Select
board, and find thepi5module. This adds the module for working with the Raspberry Pi 5's GPIO pins.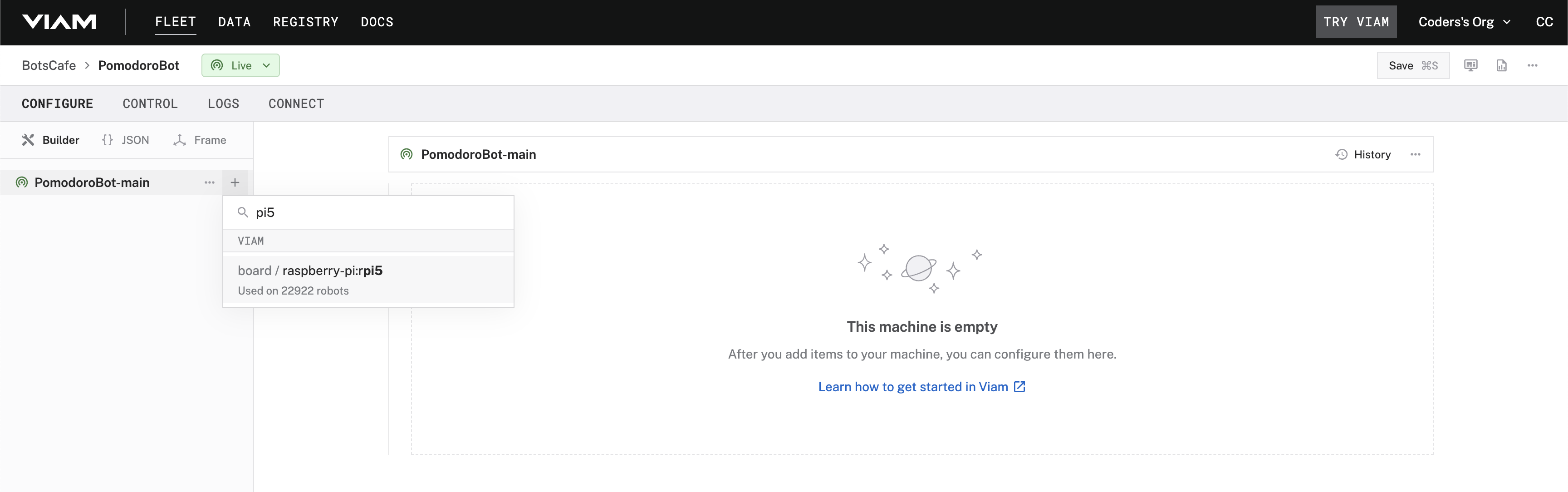
- Notice adding this module adds the board hardware component called
PI5. The collapsible card on the right corresponds to the part listed in the left sidebar.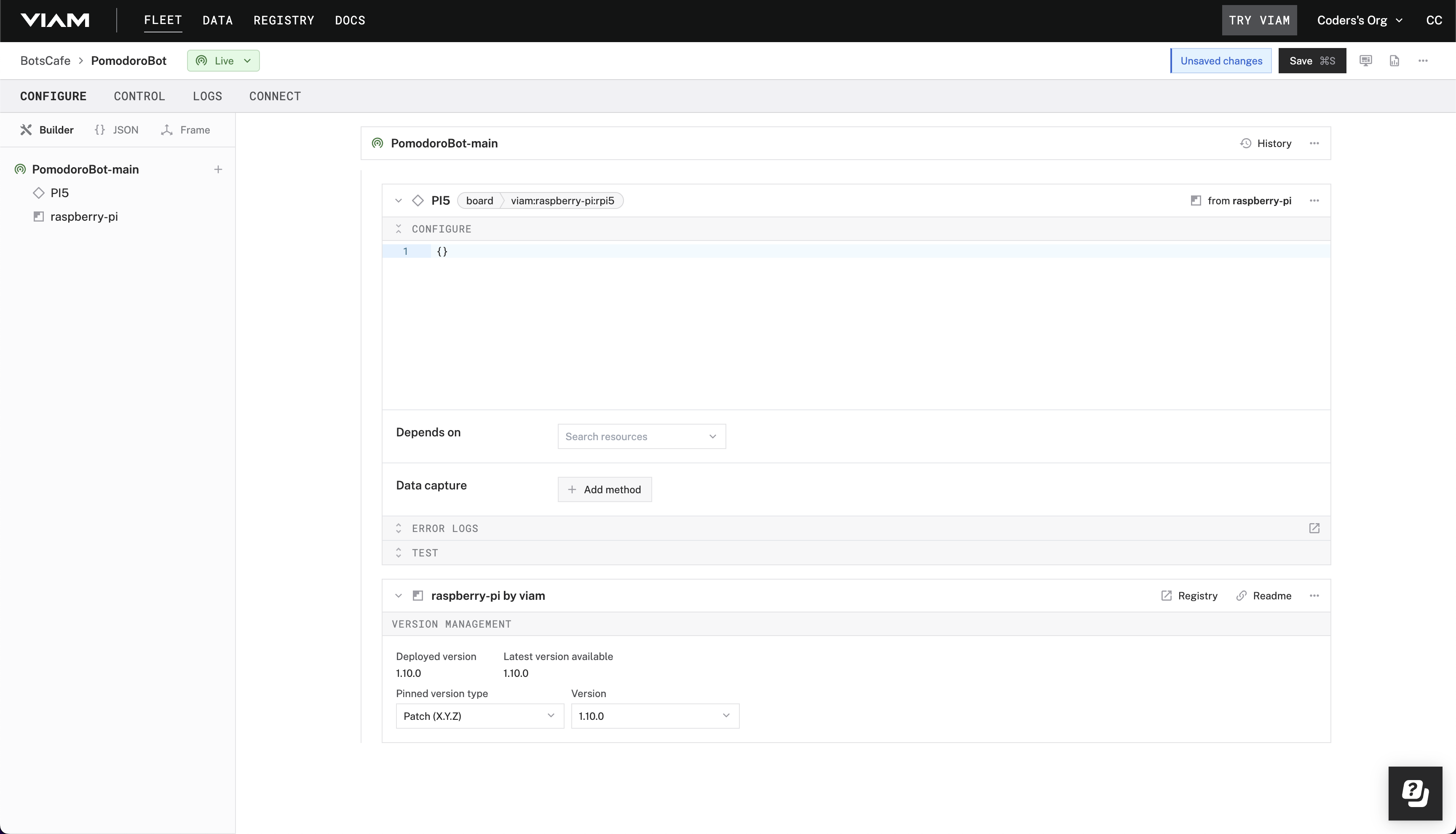
- Click Save in the top right to save and apply your configuration changes.
Now let's set up your Pomodoro Bot to work with Google Calendar, so you can stay on top of your schedule without losing focus. Once integrated, your bot will automatically sync with your calendar to manage events and reminders.
Set Up a Google Cloud Project
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Create a new project specifically for this integration.
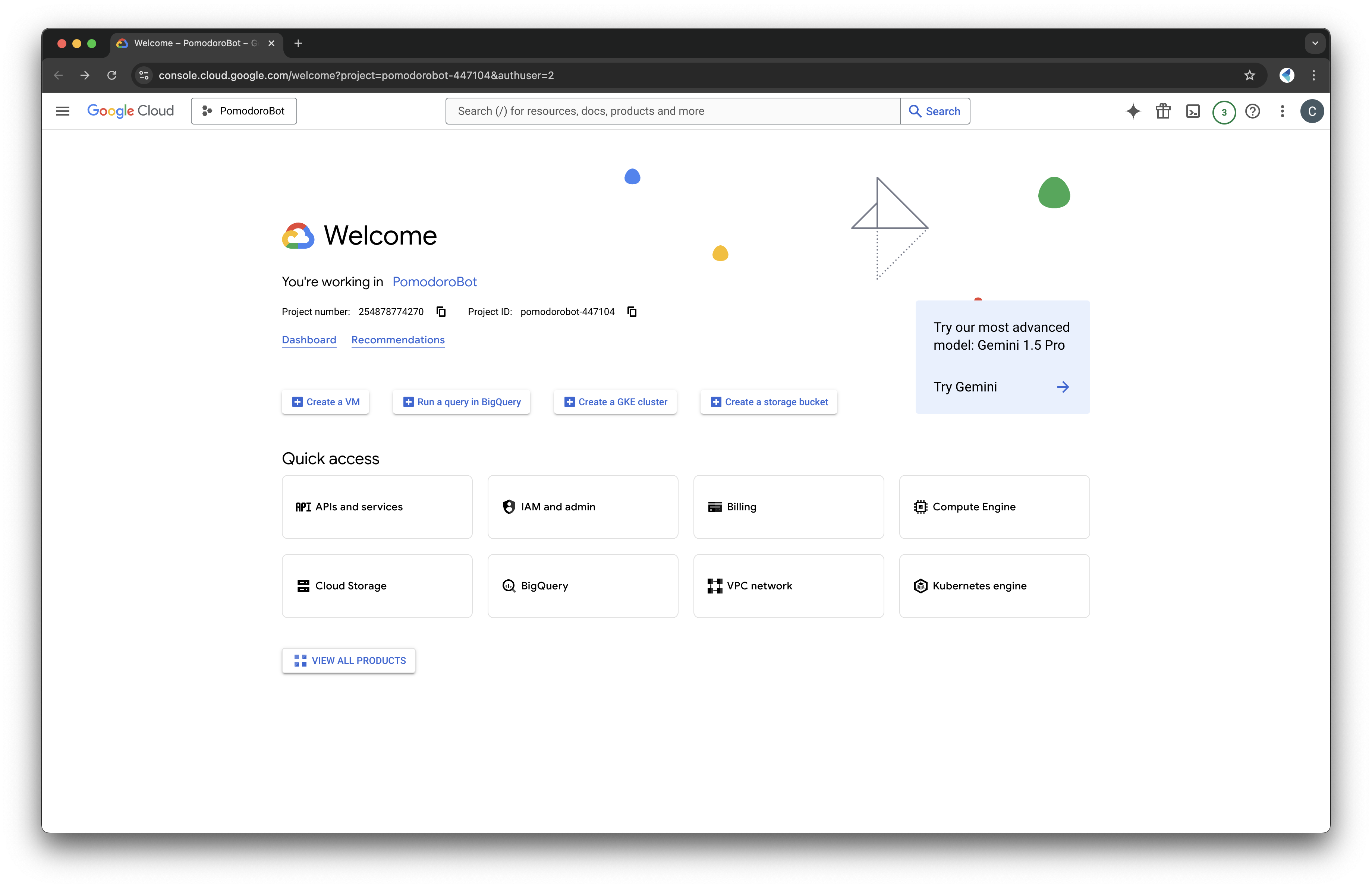
- Once the project is ready:
- Open the API Library.
- Search for "Google Calendar API".
- Click "Enable" to activate the API.
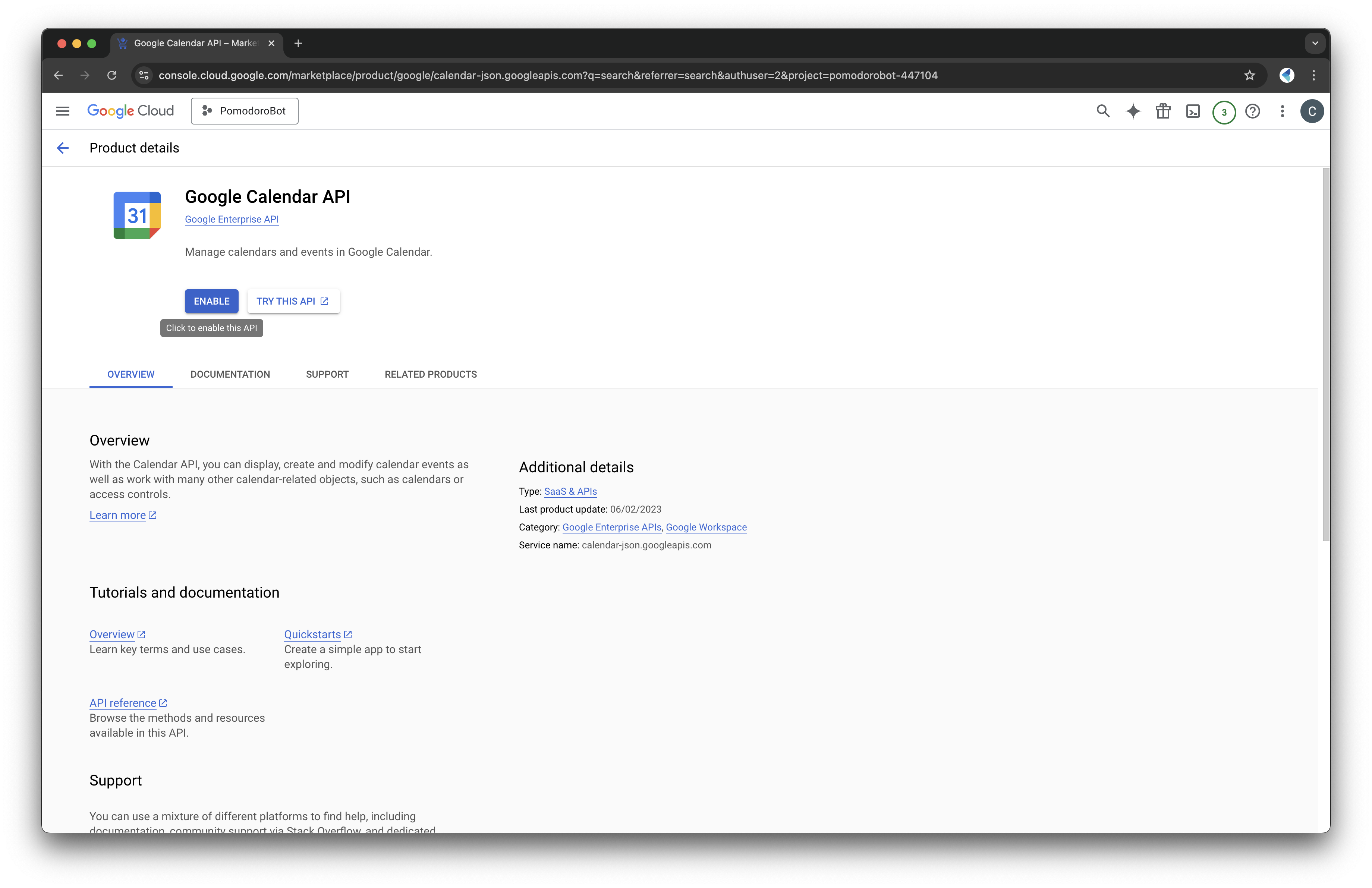
Create a Service Account
- In the Google Cloud Console, navigate to IAM & Admin > Service Accounts.
- Set up a new service account:
- Create a new service account
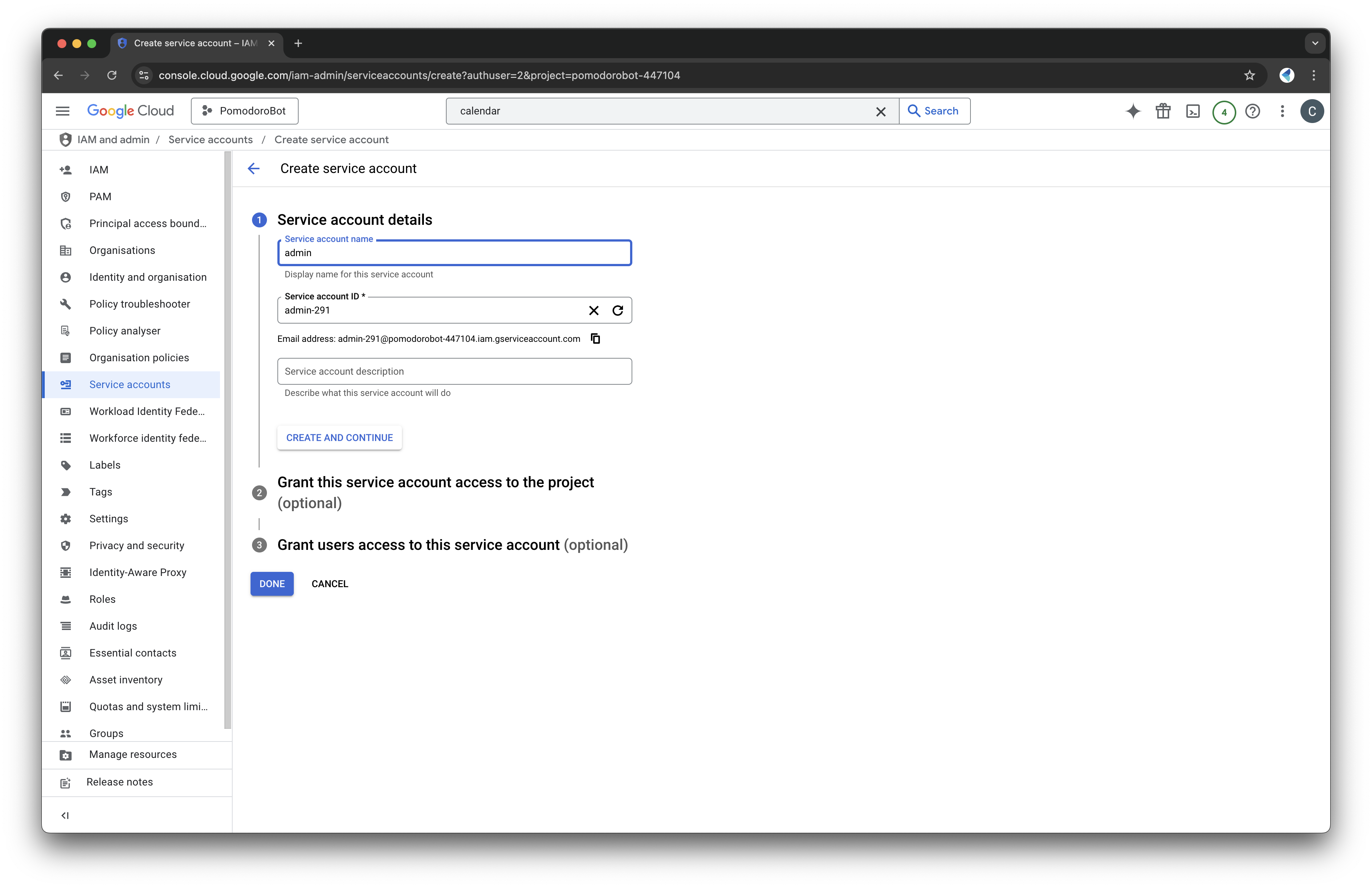
- Assign the role "Editor" or "Owner" to give it the necessary permissions.
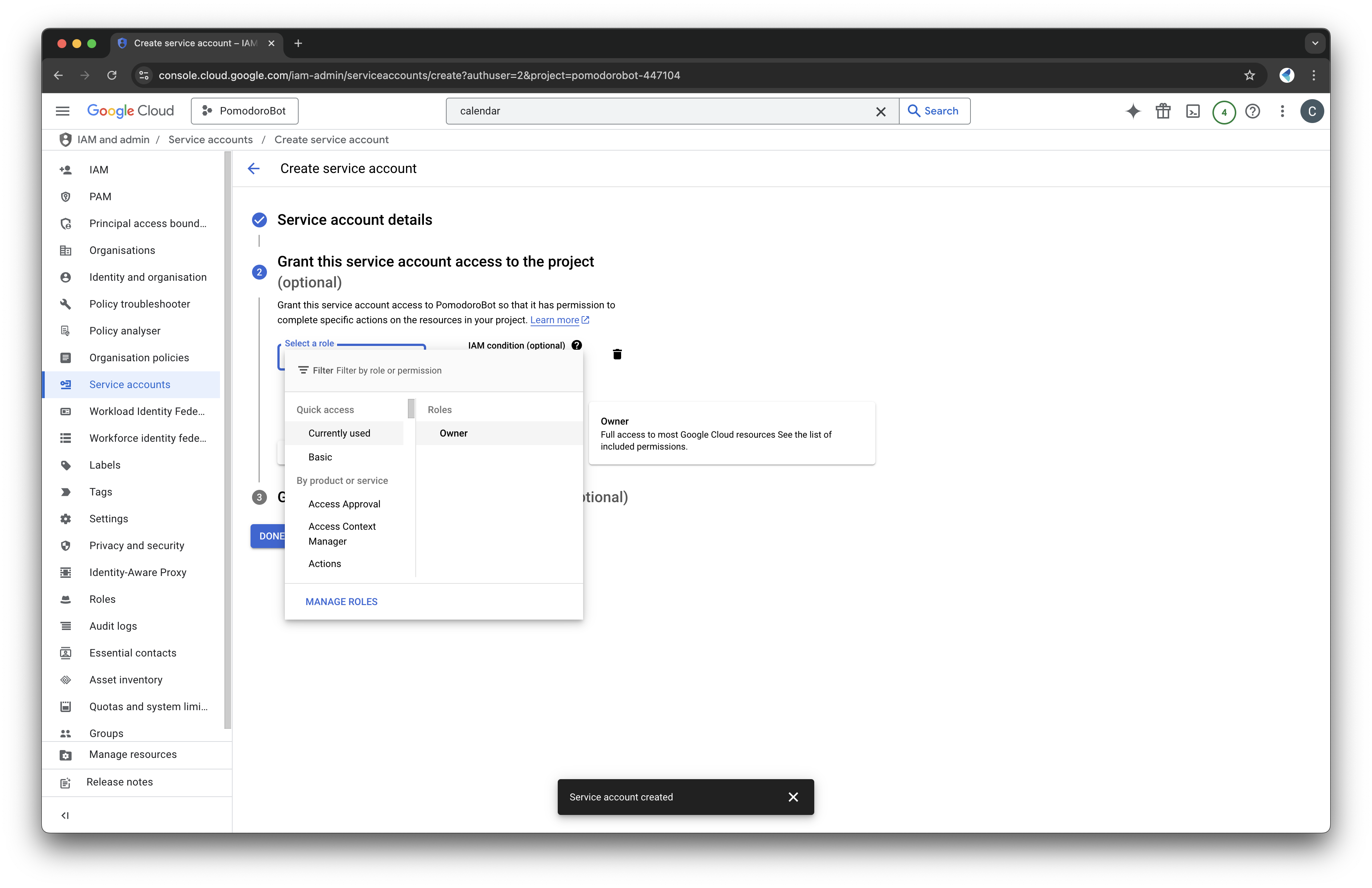
- Create and download the key file in JSON format. This file will be essential later.
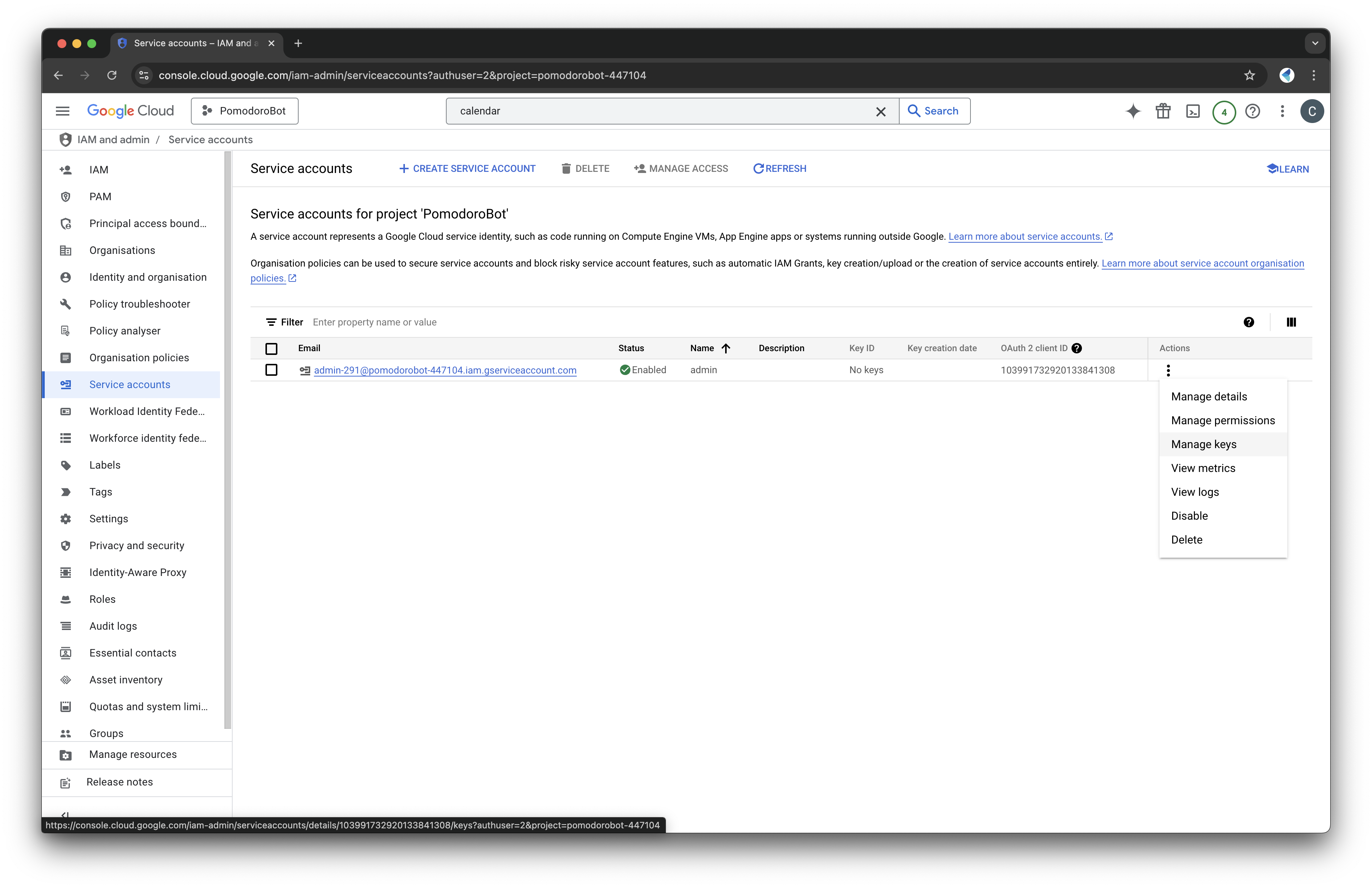
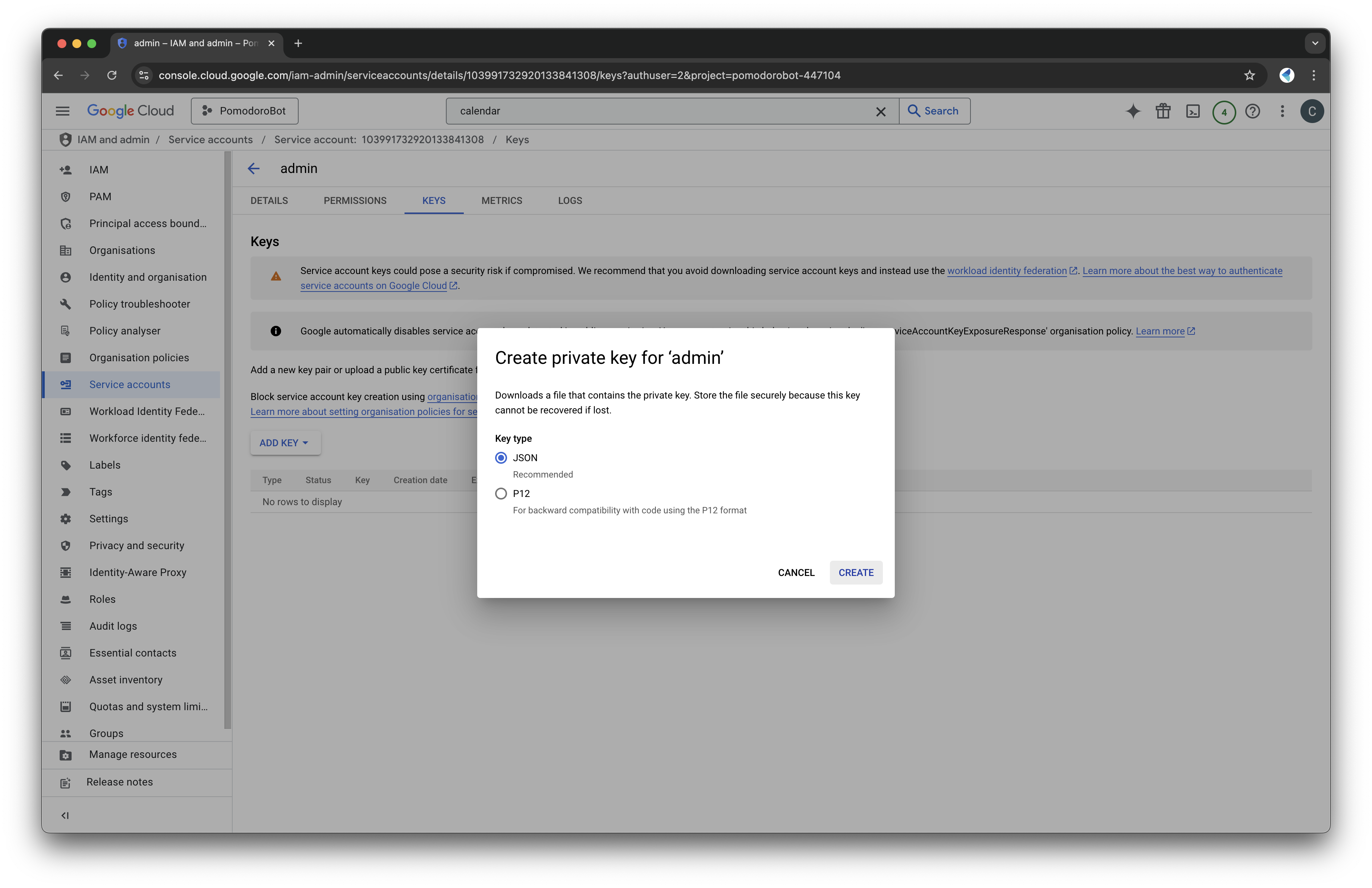
- Keep the file in a secure location.
- To transfer this file from your PC to Raspberry Pi, you can use SCP command in the following format
Using hostname
Using IP Address#Format: scp service-account-file.json username@hostname.local:/path/on/raspberrypi scp pomodorobot-service-account-file.json pi@raspberrypi.local:/home/pi/#Format: scp service-account-file-name.json username@ip-address-of-raspberrypi:/path/on/raspberrypi scp pomodorobot-service-account-file.json pi@192.168.1.4:/home/pi/
- Create a new service account
Share Your Calendar with the Service Account
- Open Google Calendar.
- Select the calendar you want to use.
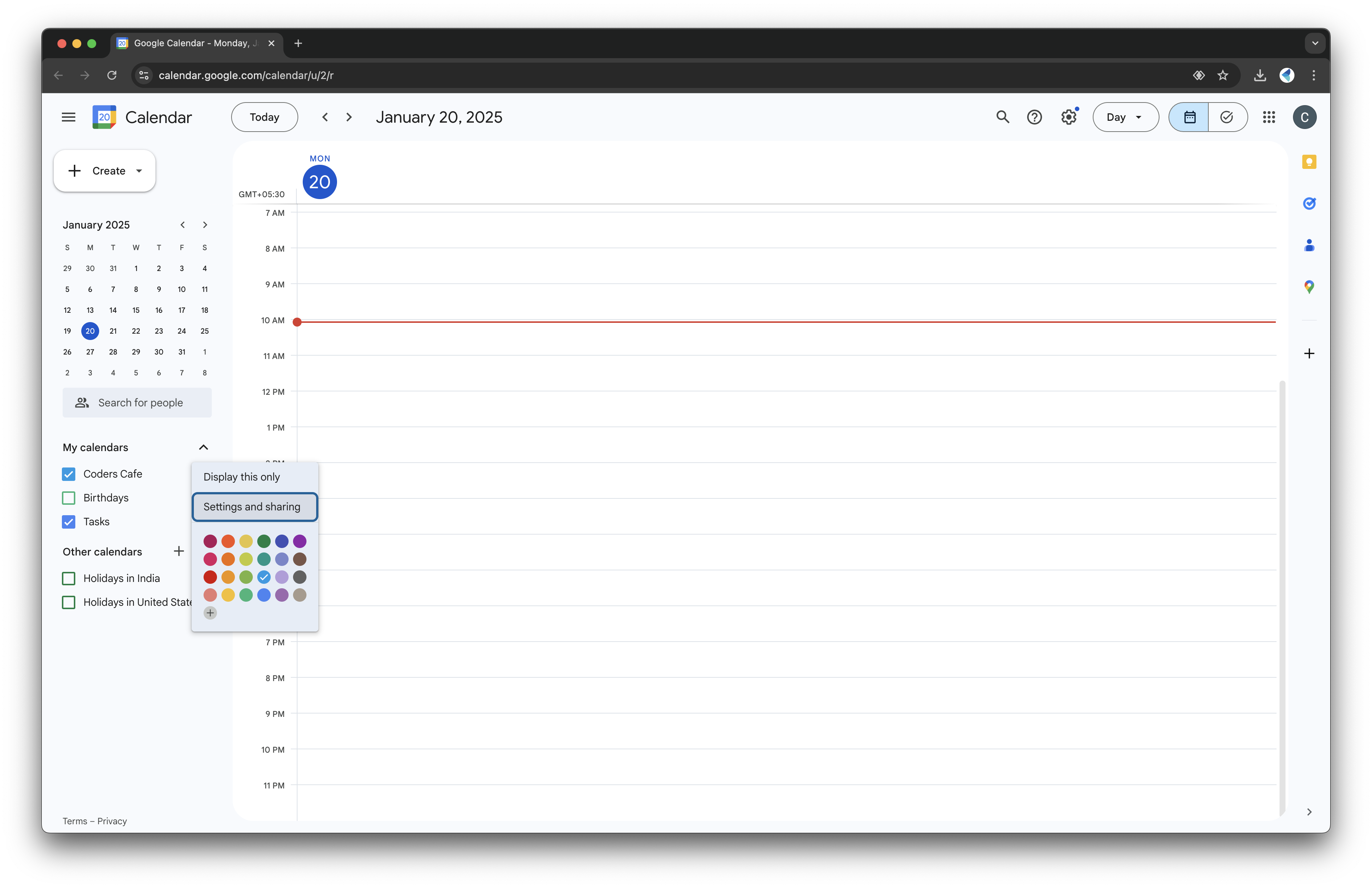
- In Settings and Sharing, find the "Share with specific people" section:
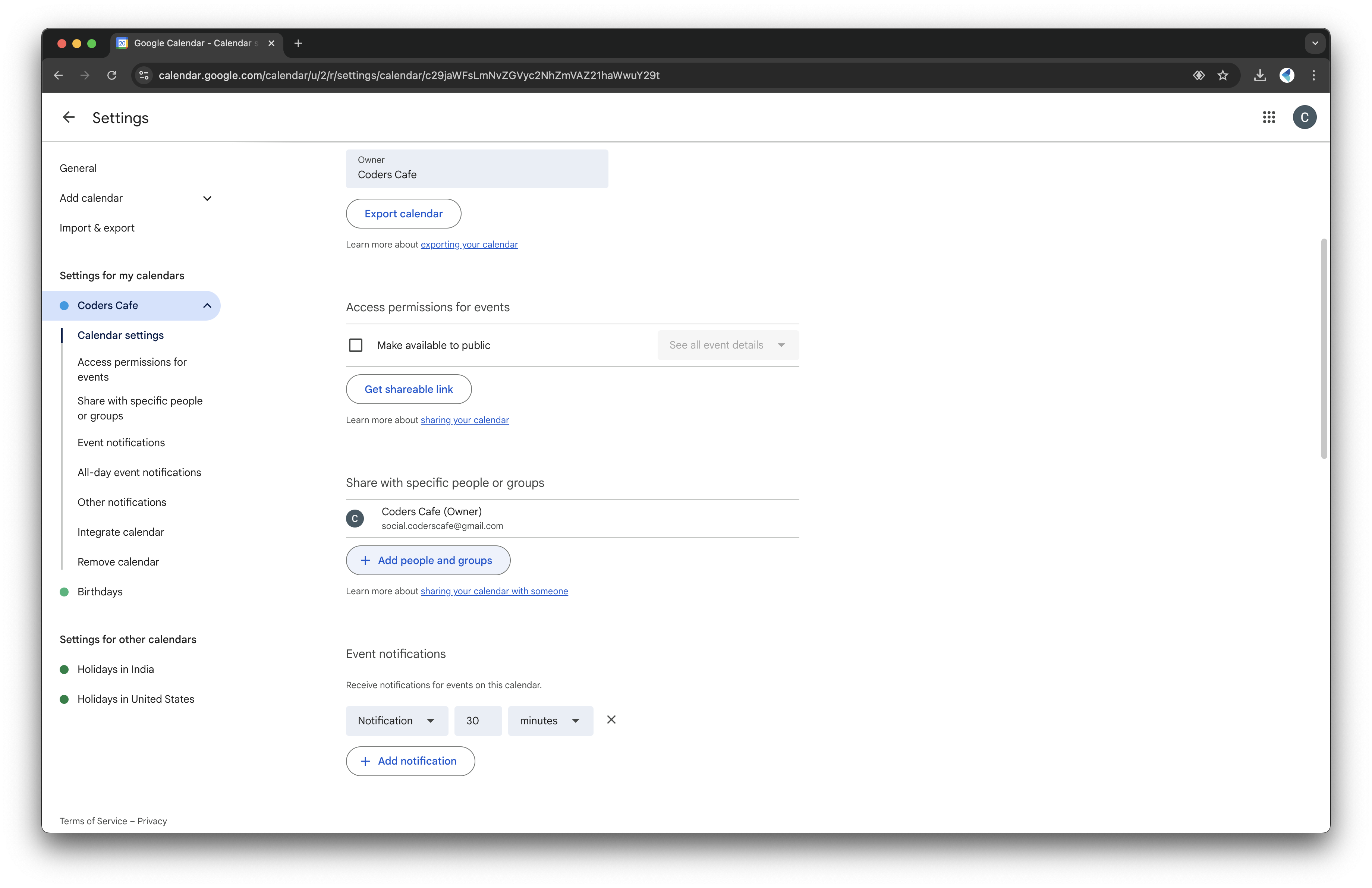
- Enter the email address from the service account key file.
- Give it permission to "Make changes to events."
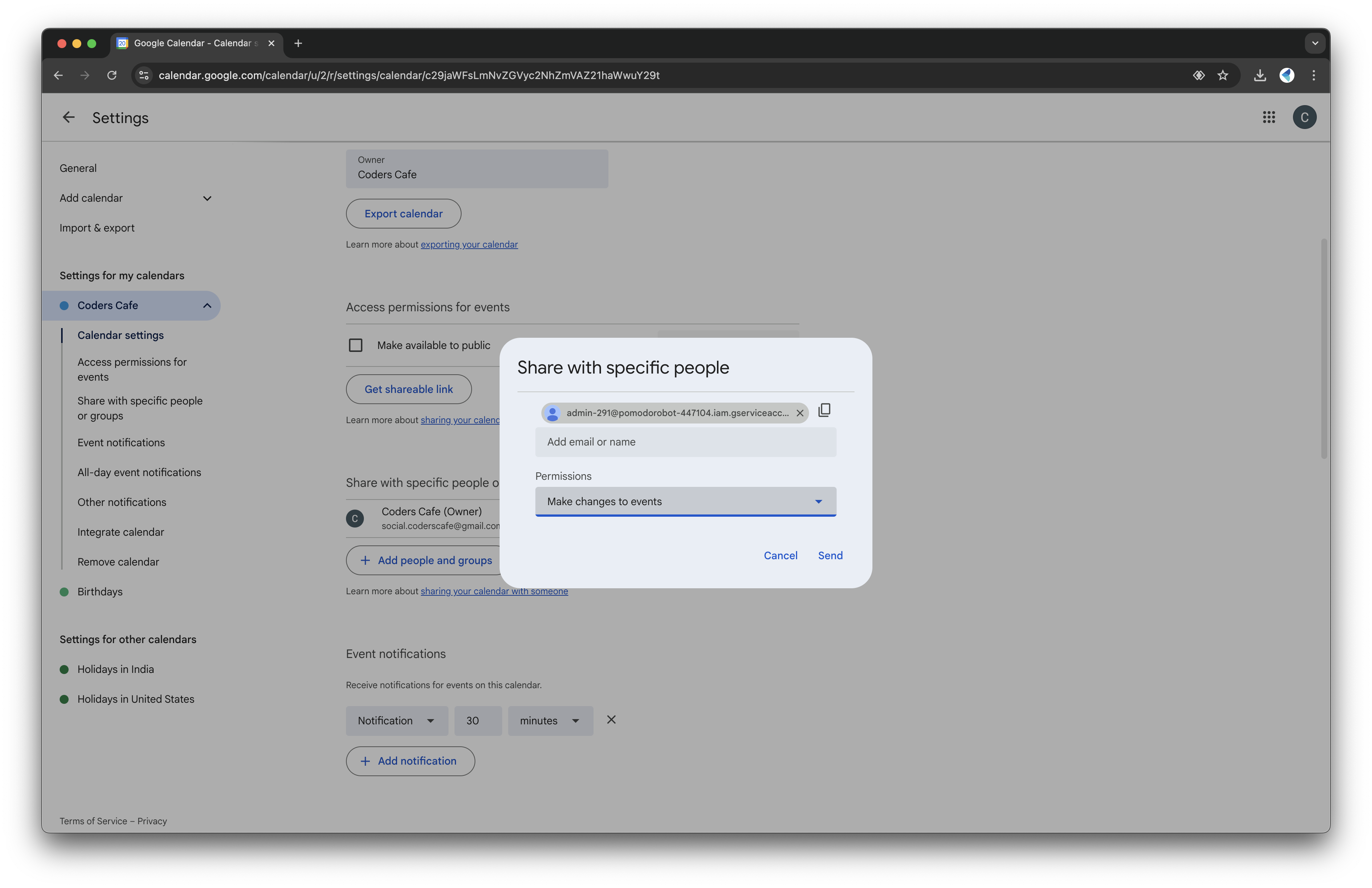
- Scroll down to "Integrate Calendar" and copy the Calendar ID for the next steps.
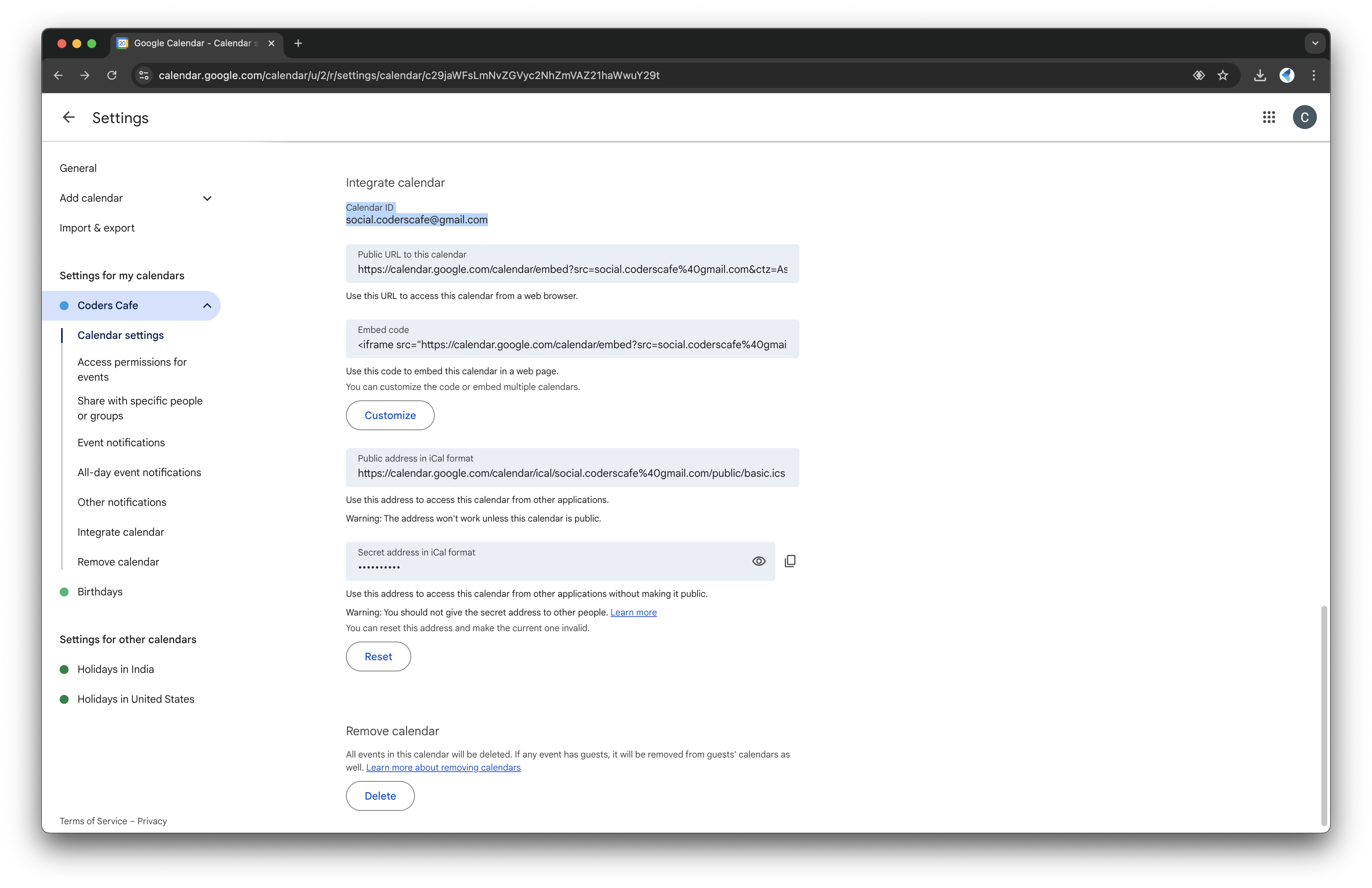
Connect Your Calendar to the Pomodoro Bot
- Open the Viam app and go to the CONFIGURE tab.
- Add the Calendar module, and provide:
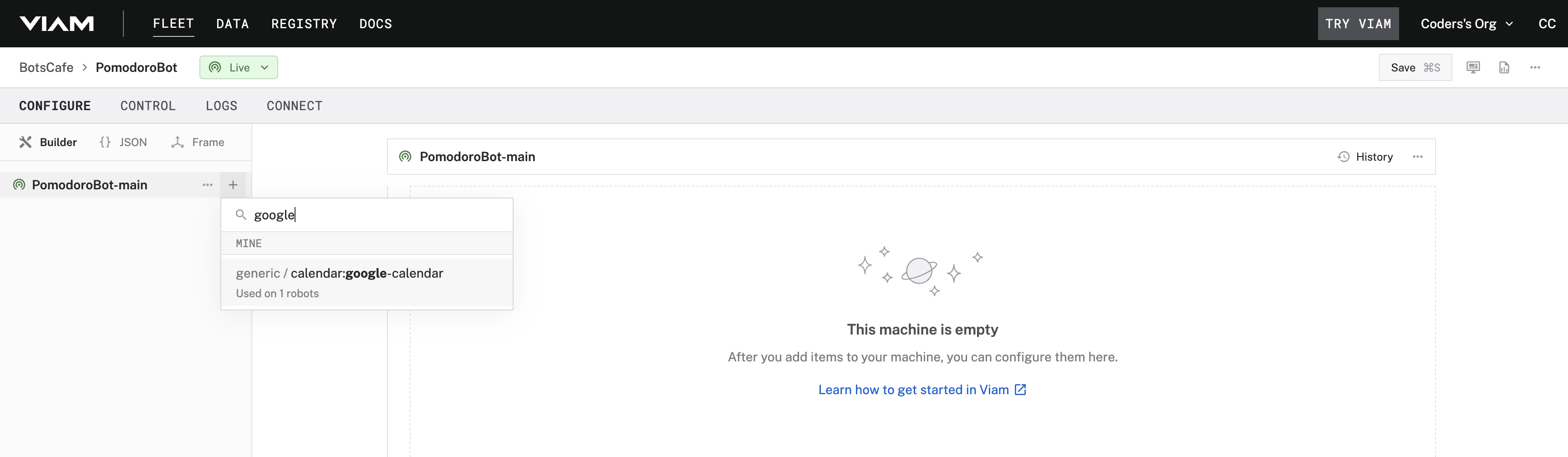
- The Calendar ID you copied earlier.
- The path to the service account JSON file.
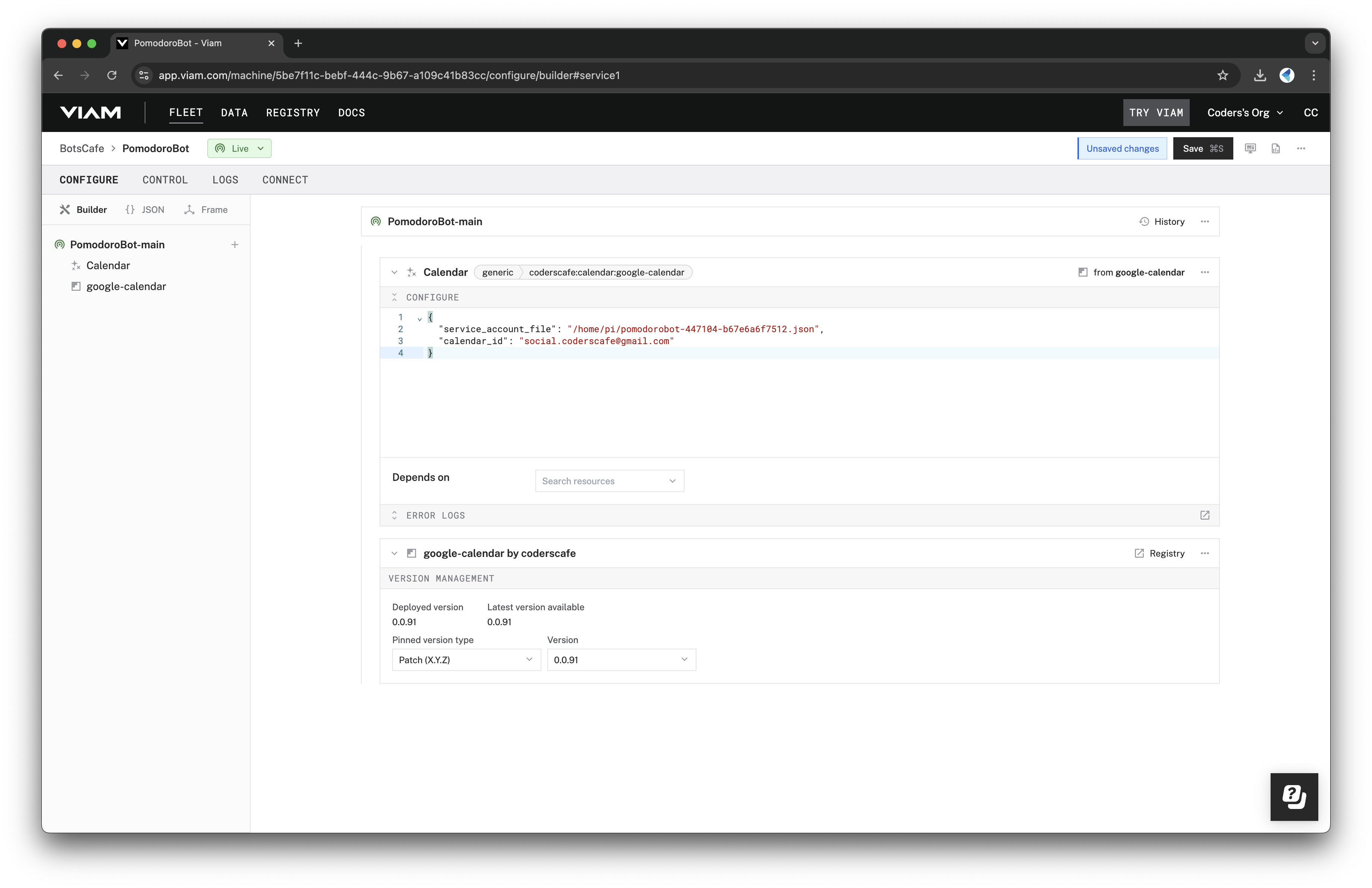
- Save your changes to complete the setup.
Test the Integration
- Create a test event in Google Calendar:
- Name it something like "Test Meeting" and save the event.
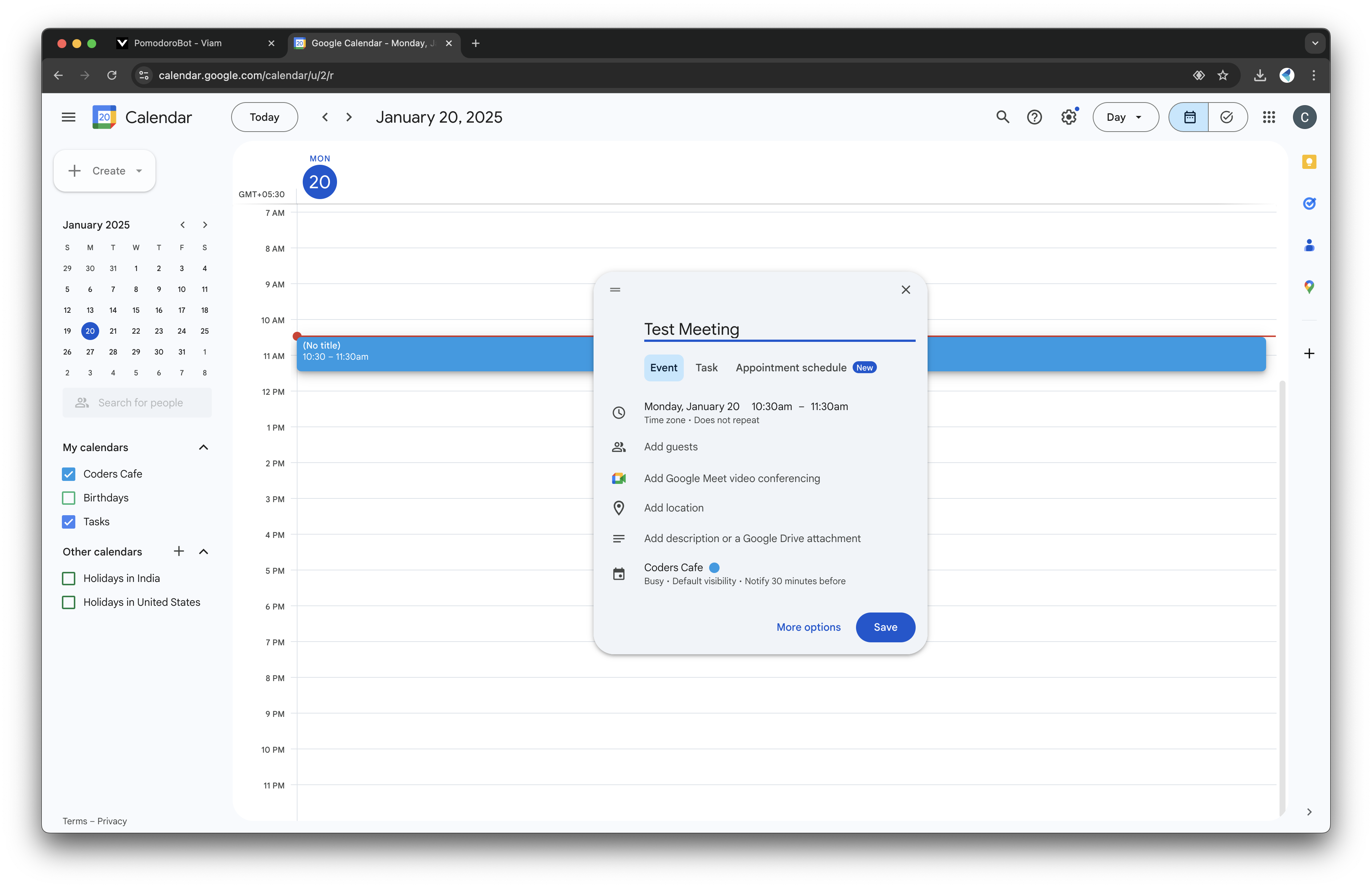
- Name it something like "Test Meeting" and save the event.
- Go back to the Viam app and open the Control tab.
- Use the given command in the DO COMMAND interface to check for upcoming calendar events.
{ "get_events": { "max_results": 10 } }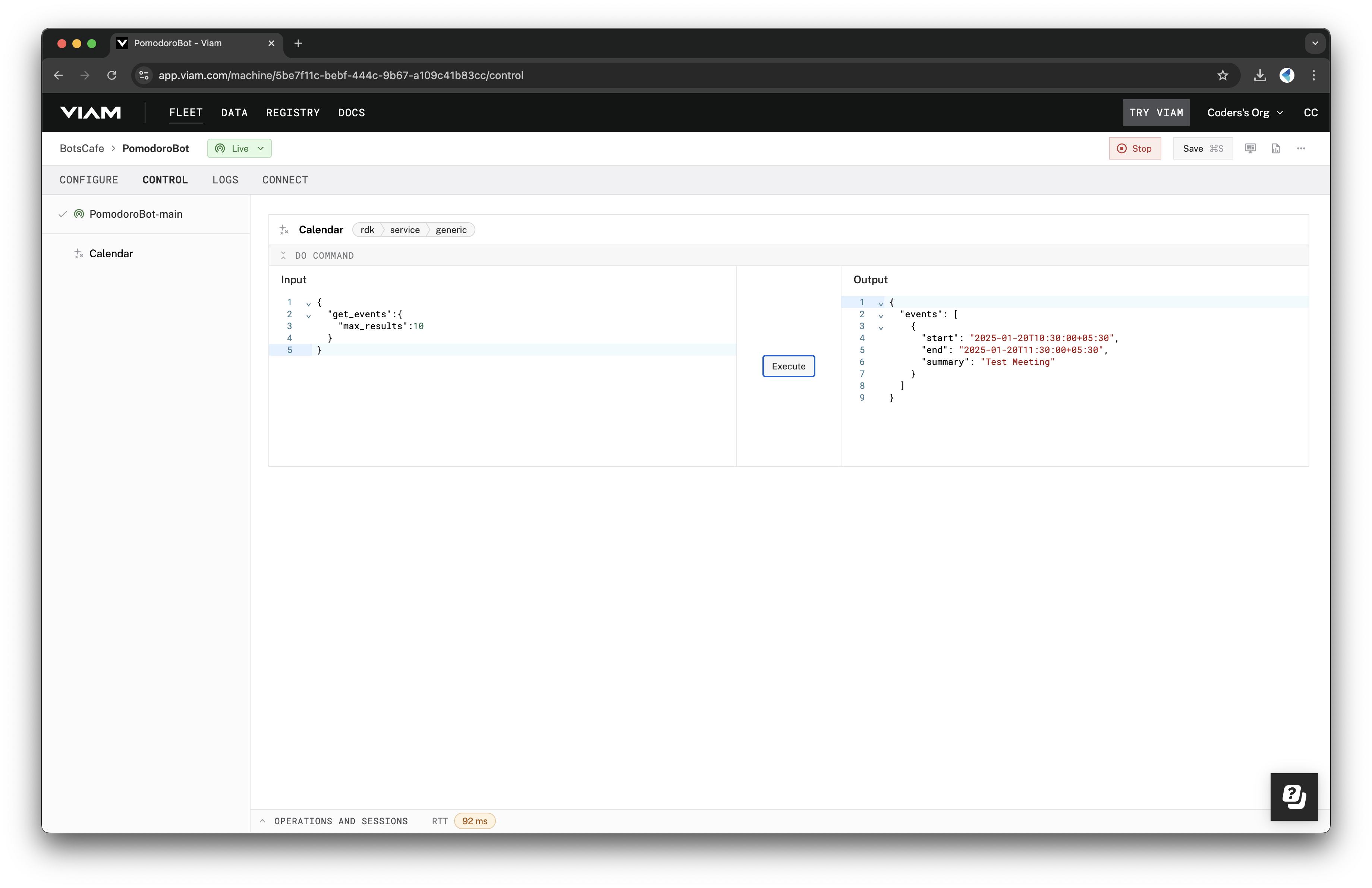
If everything is working correctly, you should see your test event ("Test Meeting") listed in the results. This confirms that your Pomodoro Bot is successfully linked to your Google Calendar.
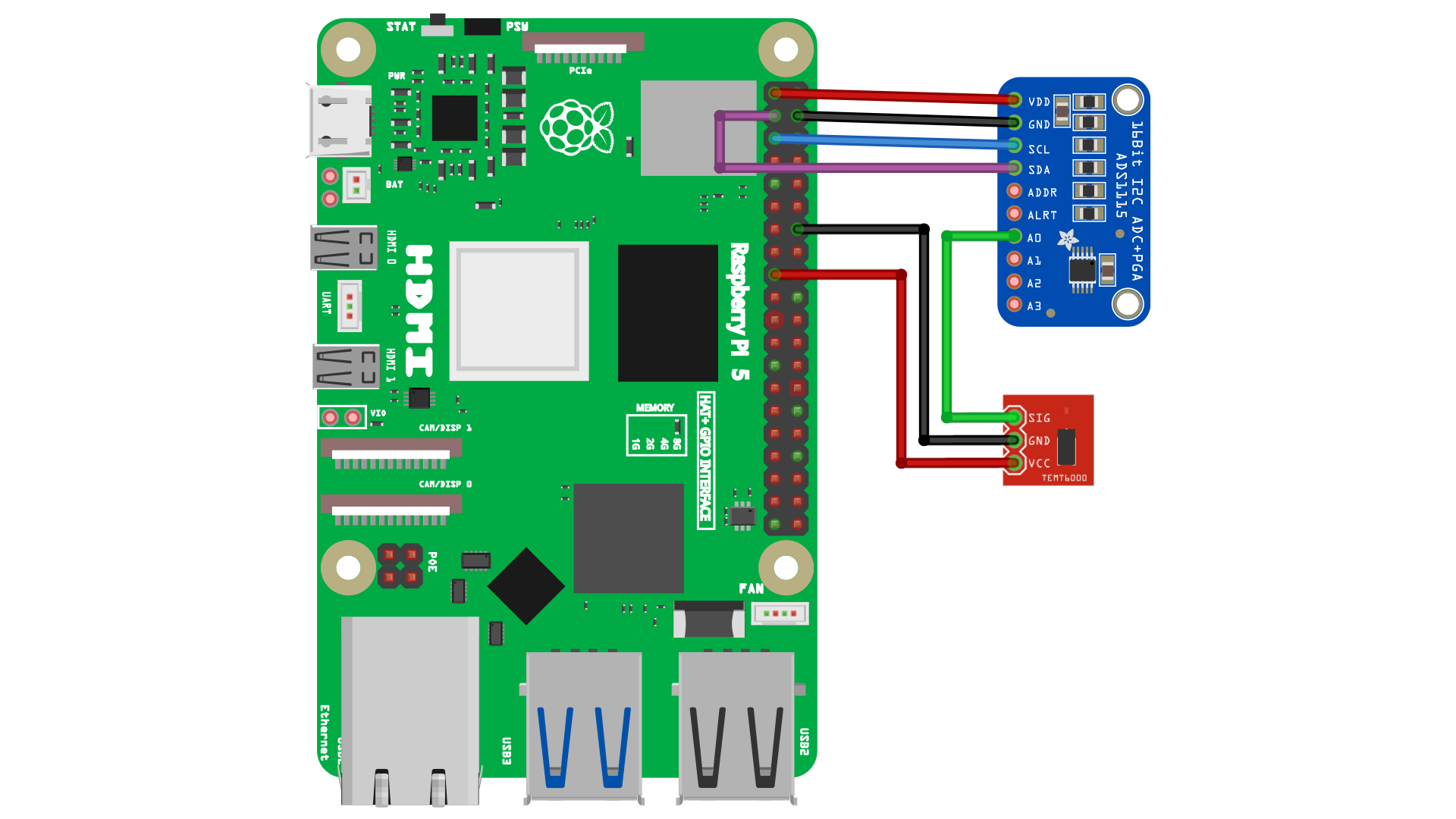
Let's integrate the ENS160 air quality sensor with your Pomodoro Bot to monitor indoor air quality effectively. The ENS160 sensor tracks VOCs (volatile organic compounds), eCO2 (equivalent carbon dioxide), and provides an Air Quality Index (AQI) – vital for maintaining an optimal workspace environment.
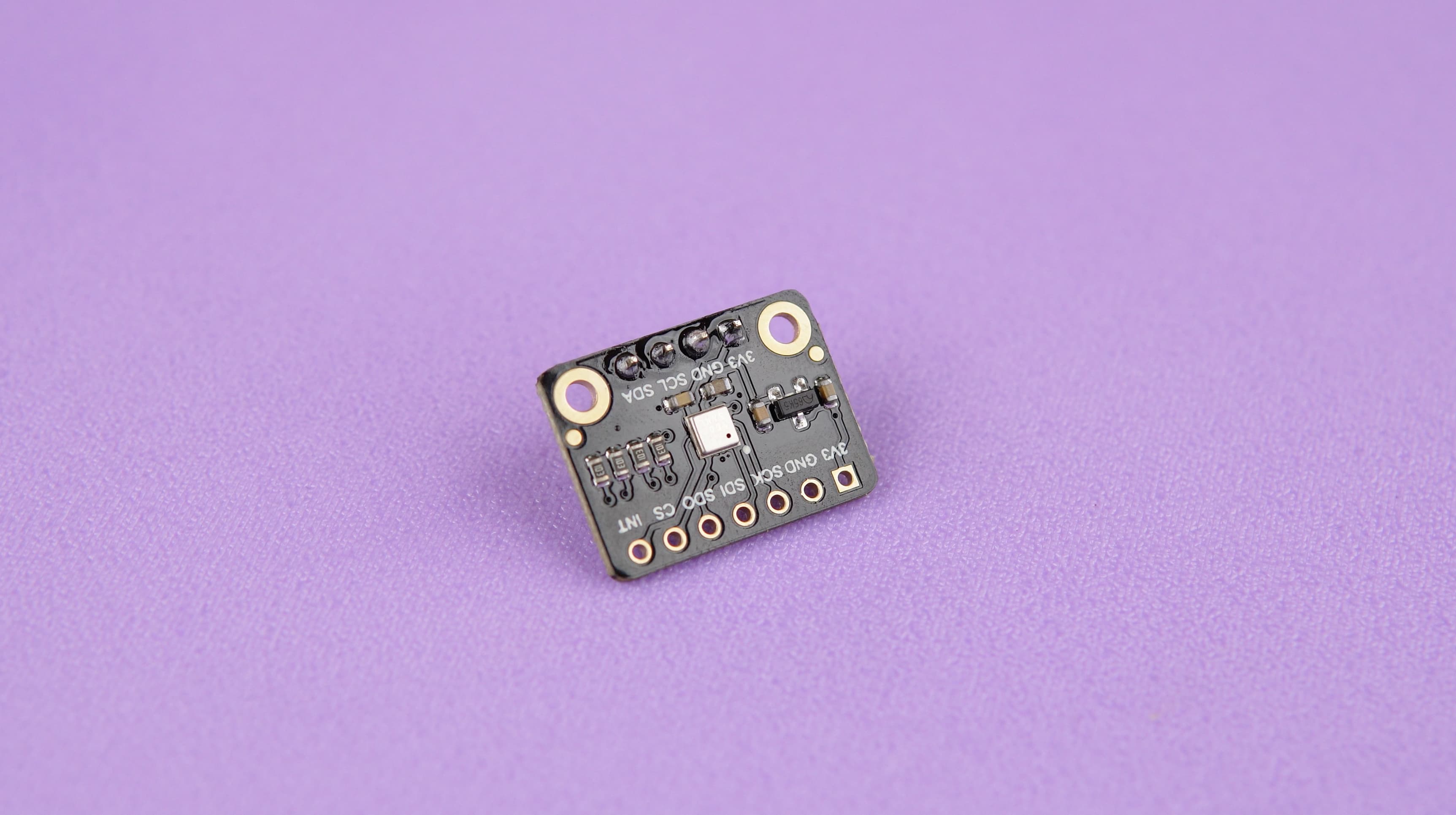
Hardware Setup
- Power Connections:
- I2C Communication:
Ensure all connections are secure and double-check your wiring to avoid any issues.
Software Integration
- Add the ENS160 Sensor to the Viam App:
- Open the Viam app.
- Navigate to the CONFIGURE tab.
- Add a new component for the ENS160 sensor.
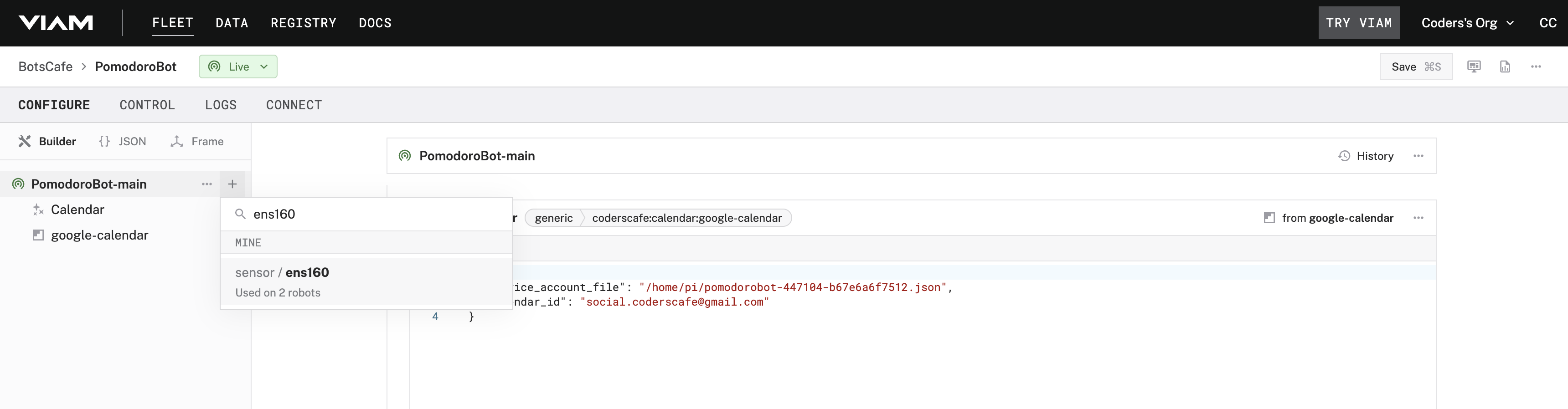
- Click "Save" and wait for the component to finish setup.
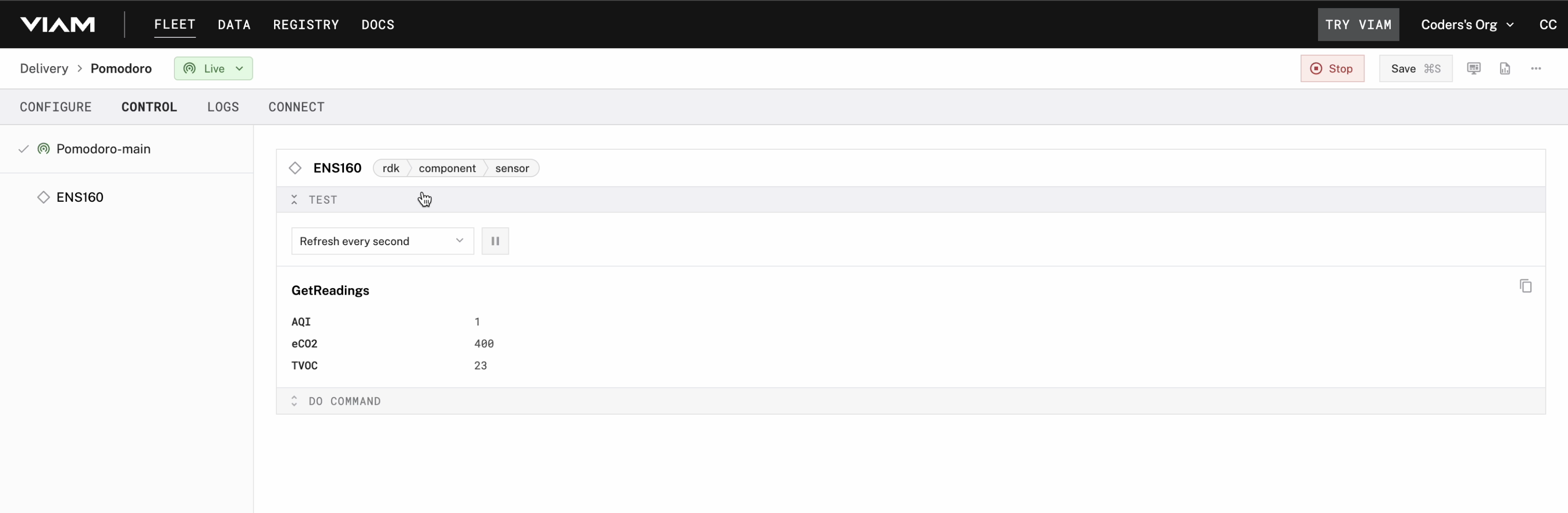
- Testing the Integration:
- Switch to the Control tab in the Viam app.
- Observe the live data feed from the ENS160 sensor, including real-time air quality metrics such as VOC levels, eCO2 values, and AQI.
Enhance your Pomodoro Bot by integrating the TEMT6000 ambient light sensor, which monitors light levels to help optimize workspace lighting for improved productivity. With this sensor, your bot can detect ambient light intensity and make adjustments as necessary to create a comfortable and efficient working environment.
Hardware Setup
- Components:
- TEMT6000 Ambient Light Sensor
- ADS1115 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- TEMT6000 Ambient Light Sensor
- Connections:
- TEMT6000 to ADS1115:
- Connect the
SorSIGPin(analog output pin) of the TEMT6000 to one of the analog input channels (e.g., A0) on the ADS1115. - Connect the
VCCpin of the TEMT6000 to the3.3Vpin on the Raspberry Pi. - Connect the
Groundpin of the TEMT6000 to theGroundpin on the ADS1115.
- Connect the
- ADS1115 to Raspberry Pi:
- TEMT6000 to ADS1115:
Software Integration
- Add the TEMT6000 Sensor in Viam App:
- Open the Viam application.
- Navigate to the CONFIGURE tab.
- Add the TEMT6000 sensor as a new component, specifying its ADC channel.
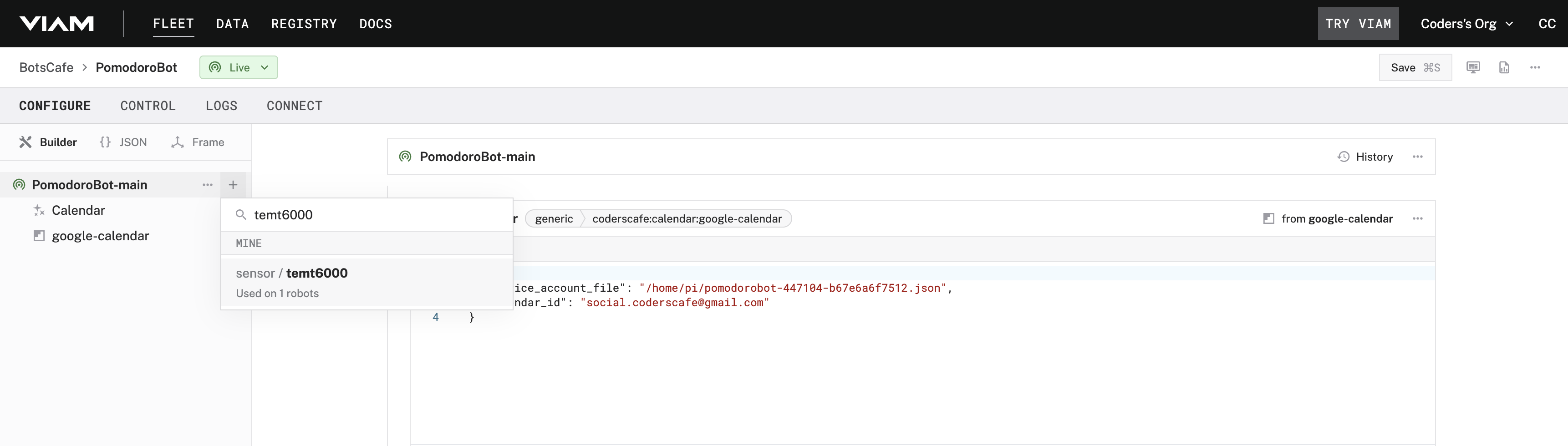
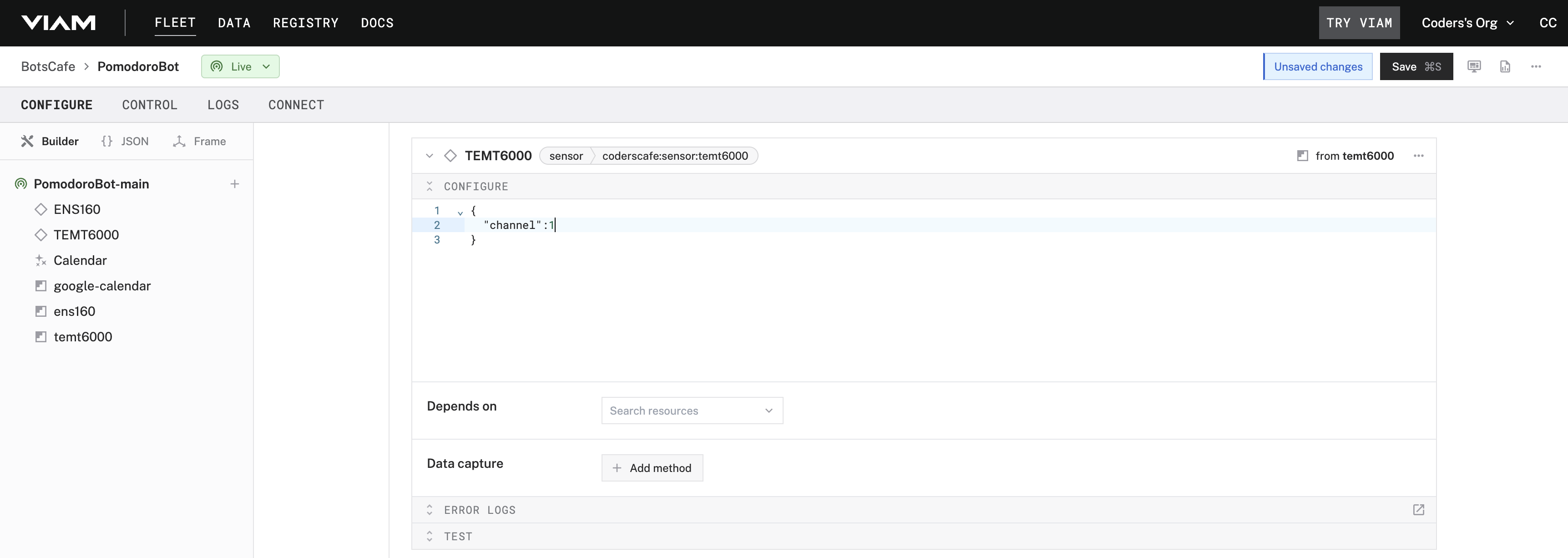
- Click "Save" and wait for the component to finish setup.
- Testing the Sensor:
- Switch to the Control tab in the Viam app.
- Observe the live data feed from the TEMT6000 sensor.
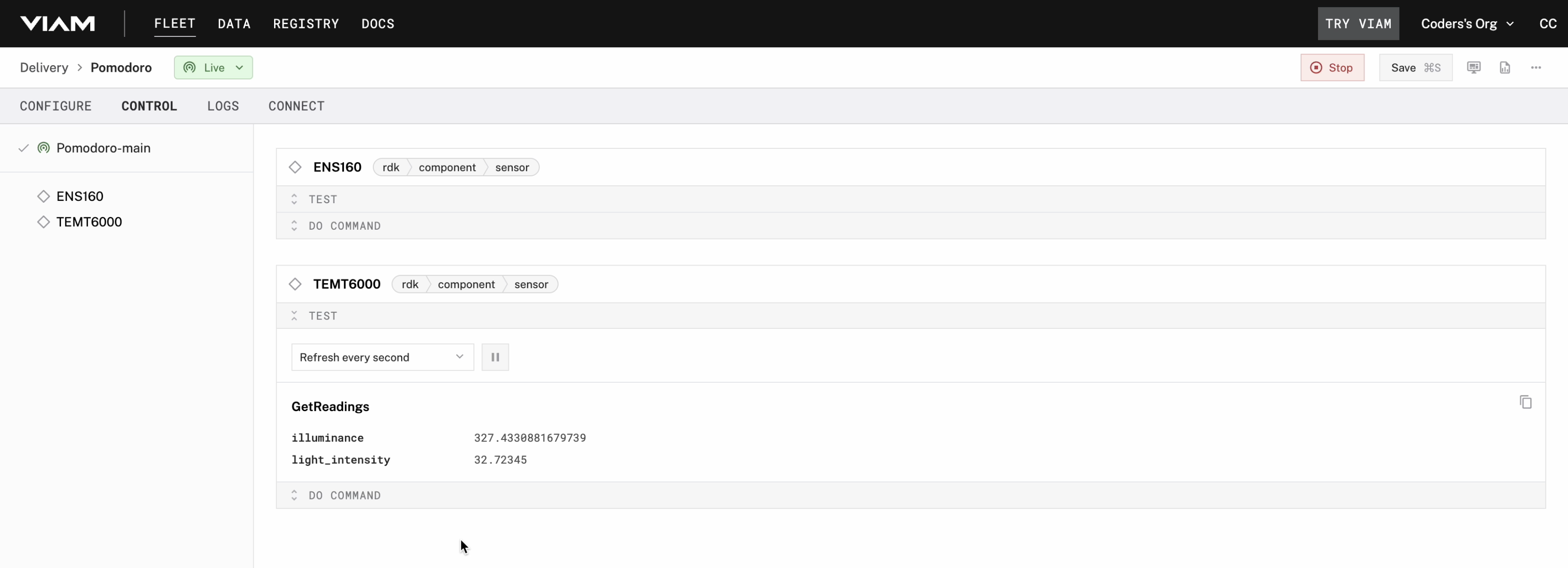
- Adjust the lighting around the sensor and verify that the readings update in real time.
Adding a display to your Pomodoro Bot elevates it from a functional productivity tool to an interactive and engaging companion. With a screen, your bot can visually communicate, provide intuitive feedback, and motivate you with friendly reminders or fun animations.
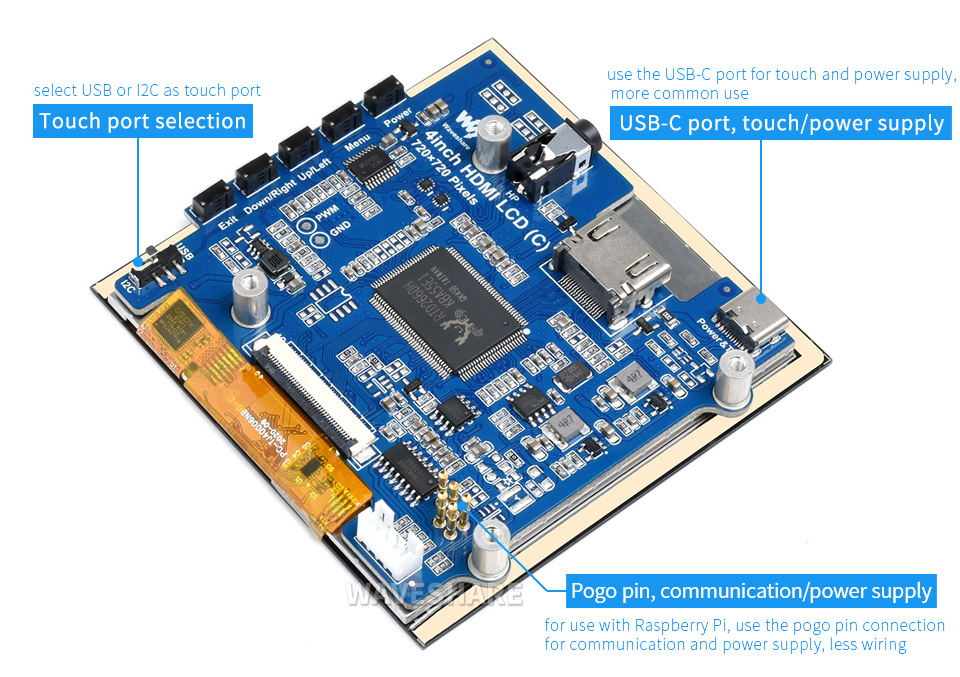
Features
- 4-inch IPS screen, hardware resolution is 720 × 720.
- 5-point capacitive touch, toughened glass panel, hardness up to 6H.
- When used with Raspberry Pi, it supports Raspberry Pi OS / Ubuntu / Kali and Retropie.
- Ubuntu is supported when used with Jetson Nano.
- When used as a computer monitor, it supports Windows 11/10/8.1/8/7.
- Onboard dual touch circuit, optional USB Type-C or I2C touch, it has more application scenarios.
- With 3.5mm audio and speaker interface, it supports HDMI audio output.
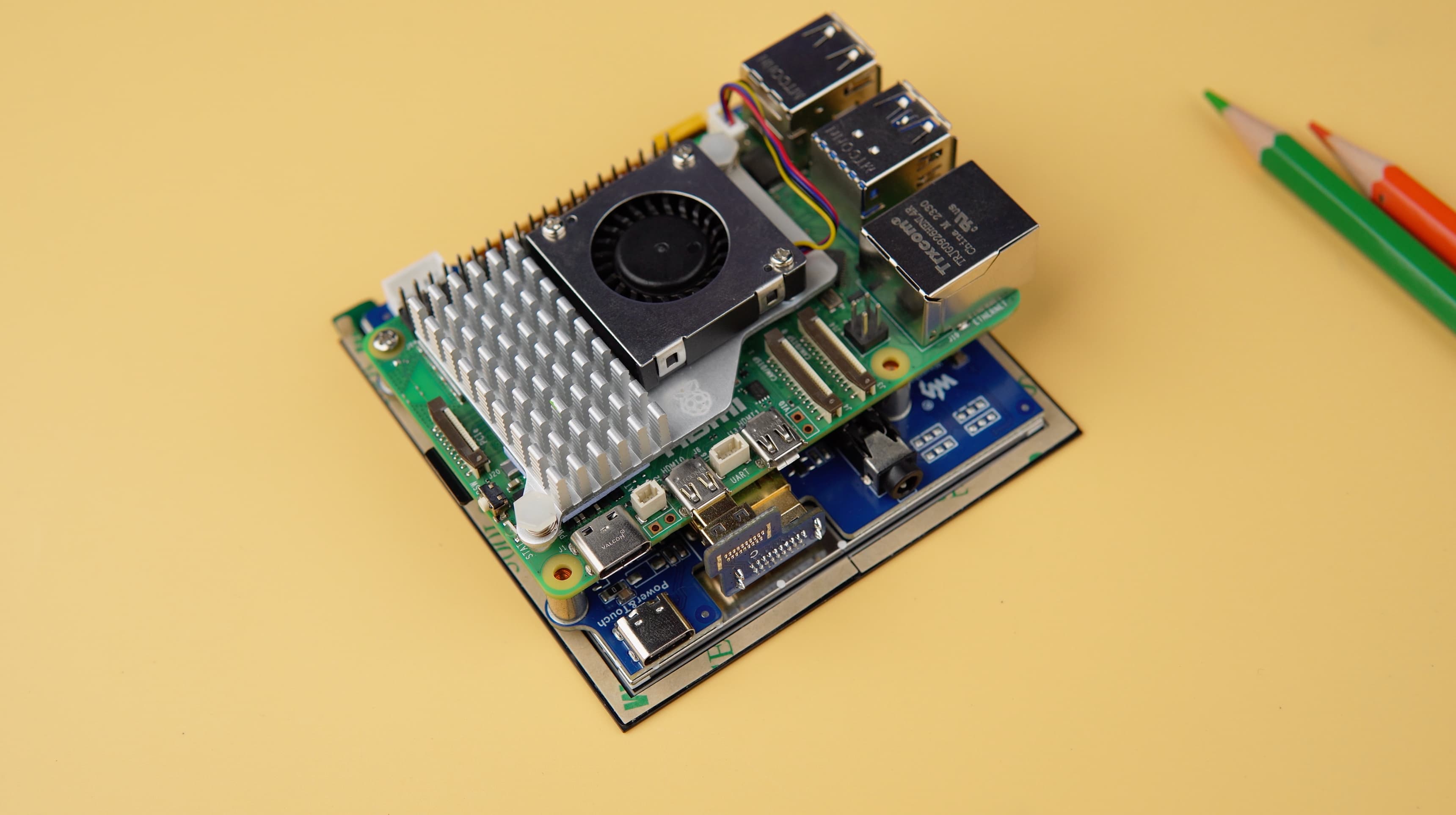
Hardware Connection
- Set the touch switch on the back of the screen to "I2C".
- Fix the Raspberry Pi to the screen through the copper posts, and pay attention to aligning the position of the ejector pins.
- Connect the HDMI port of the Raspberry Pi to the LCD.
- Connect USB-C on Display to USB port on Raspberry Pi to enable touch interactions.
Software Setup
- Follow the instructions to Setup Raspberry Pi using Pi Imager.
- After the setup is completed, insert the SD card into your computer and open the config.txt file in the root directory of the SD card, and add the following code at the end of the file:
dtparam=i2c_arm=on
dtoverlay=waveshare-4dpic-3b
dtoverlay=waveshare-4dpic-4b
dtoverlay=waveshare-4dpic-5b
hdmi_force_hotplug=1
config_hdmi_boost=10
hdmi_group=2
hdmi_mode=87
hdmi_timings=720 0 100 20 100 720 0 20 8 20 0 0 0 60 0 48000000 6
start_x=0
gpu_mem=128
- Download the 4inch HDMI LCD (C) DTBO file and extract the 3 dtbo files. Copy these 3 files to the overlays directory (
/boot/overlays/). - Save the changes to the config.txt file, eject the SD card safely, and insert it into the Raspberry Pi.
- Power on the Raspberry Pi and wait for more than ten seconds to display normally
To enhance the functionality of your Pomodoro Bot, you can integrate a push button to allow manual control, such as starting or stopping tasks, resetting timers, or triggering specific actions. Here's how to add a push button:
Hardware Setup
Components Needed:
- Push button module
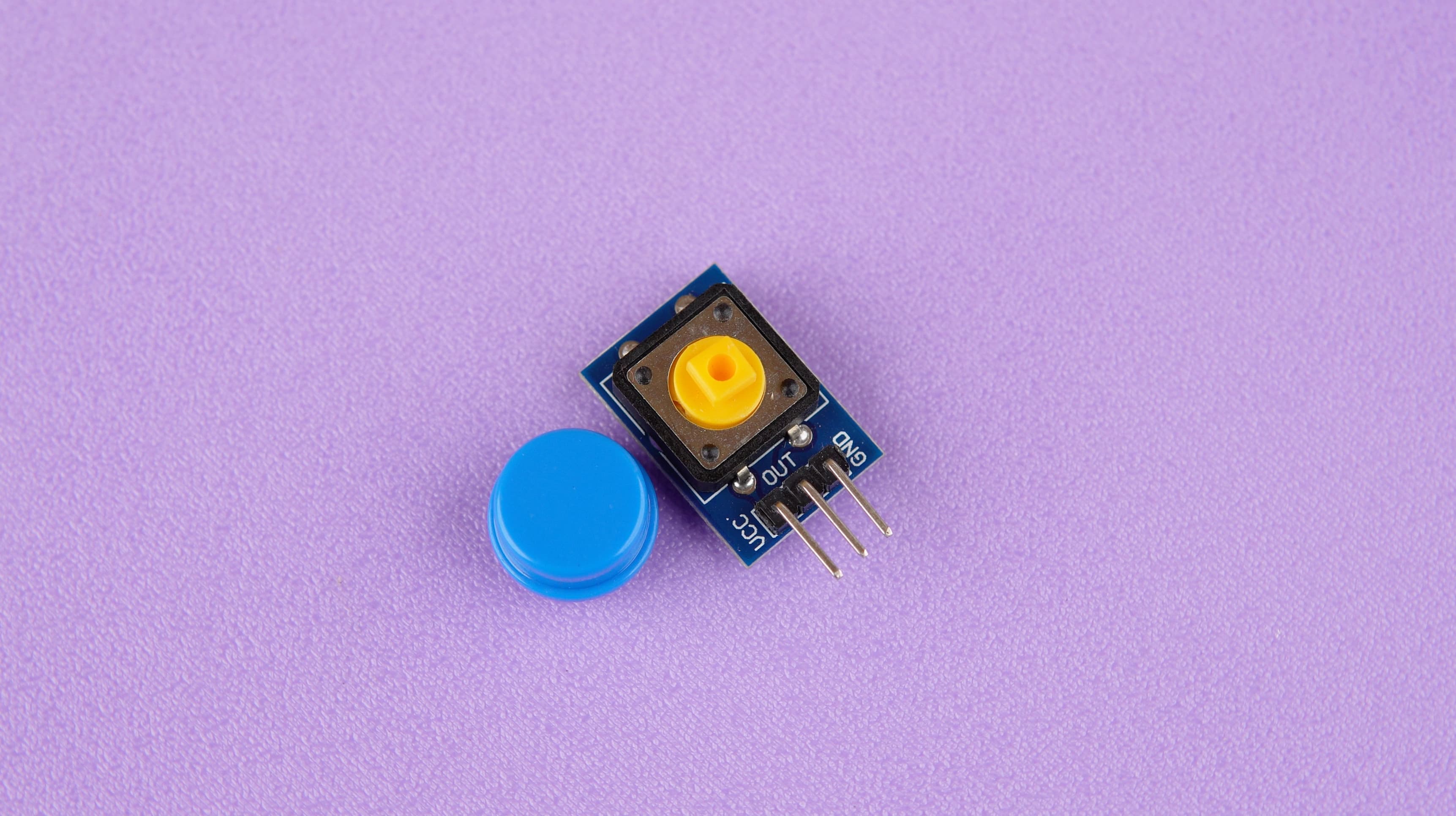
- Jumper wires
Wiring:
- Connect
VCCpin of the push button to a5Vpin on the Raspberry Pi. - Connect
GNDpin of the push button to aGroundpin on the Raspberry Pi. - Connect
OUTpin of the push button to aGPIO 17on the Raspberry Pi.
By adding a push button, you can make your Pomodoro Bot more interactive and user-friendly!
Aesthetics and Personality
We envisioned the Pomodoro Bot as more than just a functional tool. It needed to be visually appealing and possess a unique personality. To achieve this we used Fusion 360, to craft a 3D model, carefully balancing aesthetics and practicality. This process involved refining every detail to ensure the bot was both charming and functional.
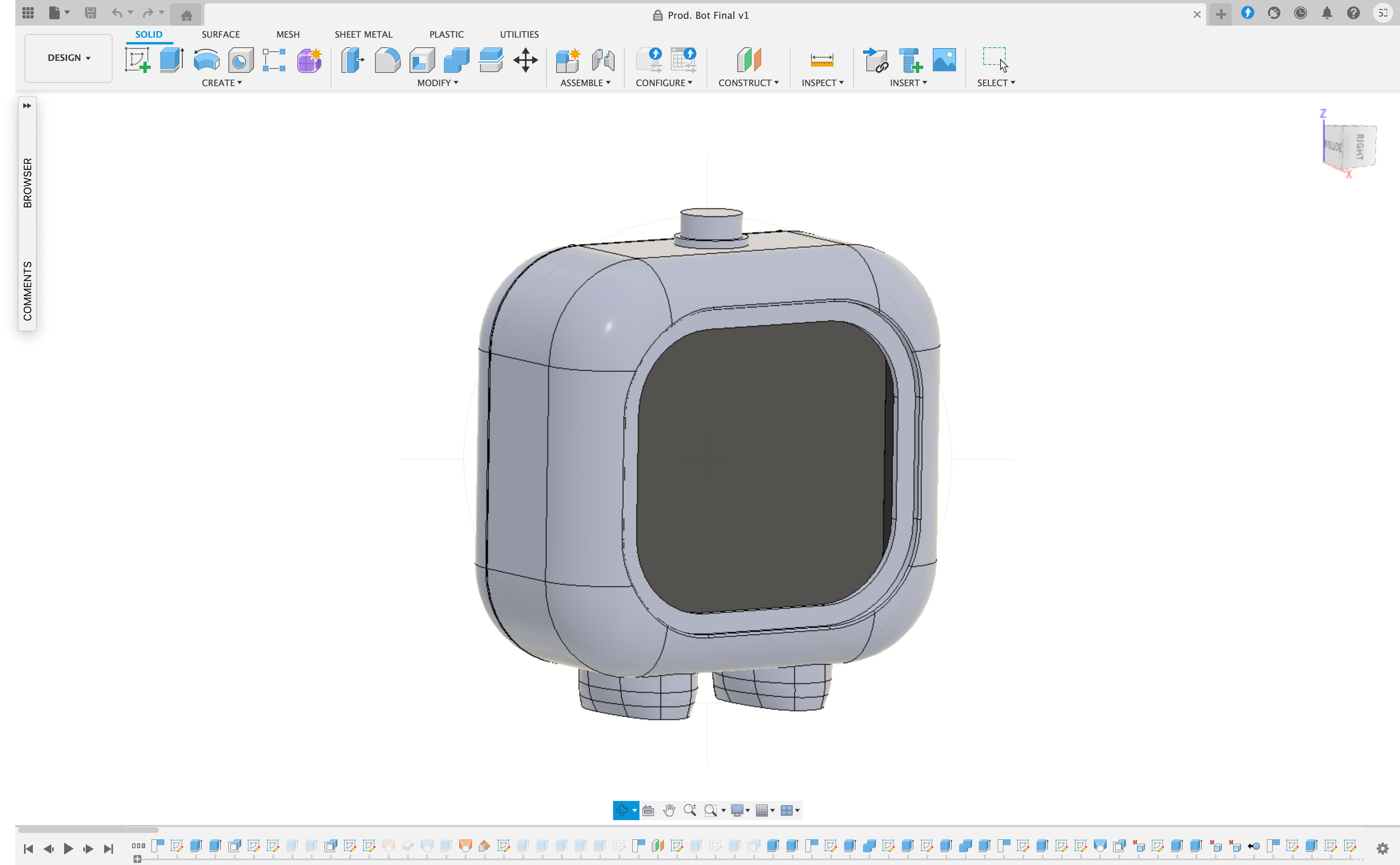
The final result is a compact and modern 3D-printed bot that is not only a productivity powerhouse but also a delightful desk companion designed to bring a smile to your face while helping you stay focused.
3D Printing Process
After finalizing the design, we brought our concept to life through 3D printing. We utilized the Bambu A1 3D printer to:
- Create the bot's physical form with precision and efficiency.
- Achieve a durable and well-crafted model that perfectly matched our design vision.
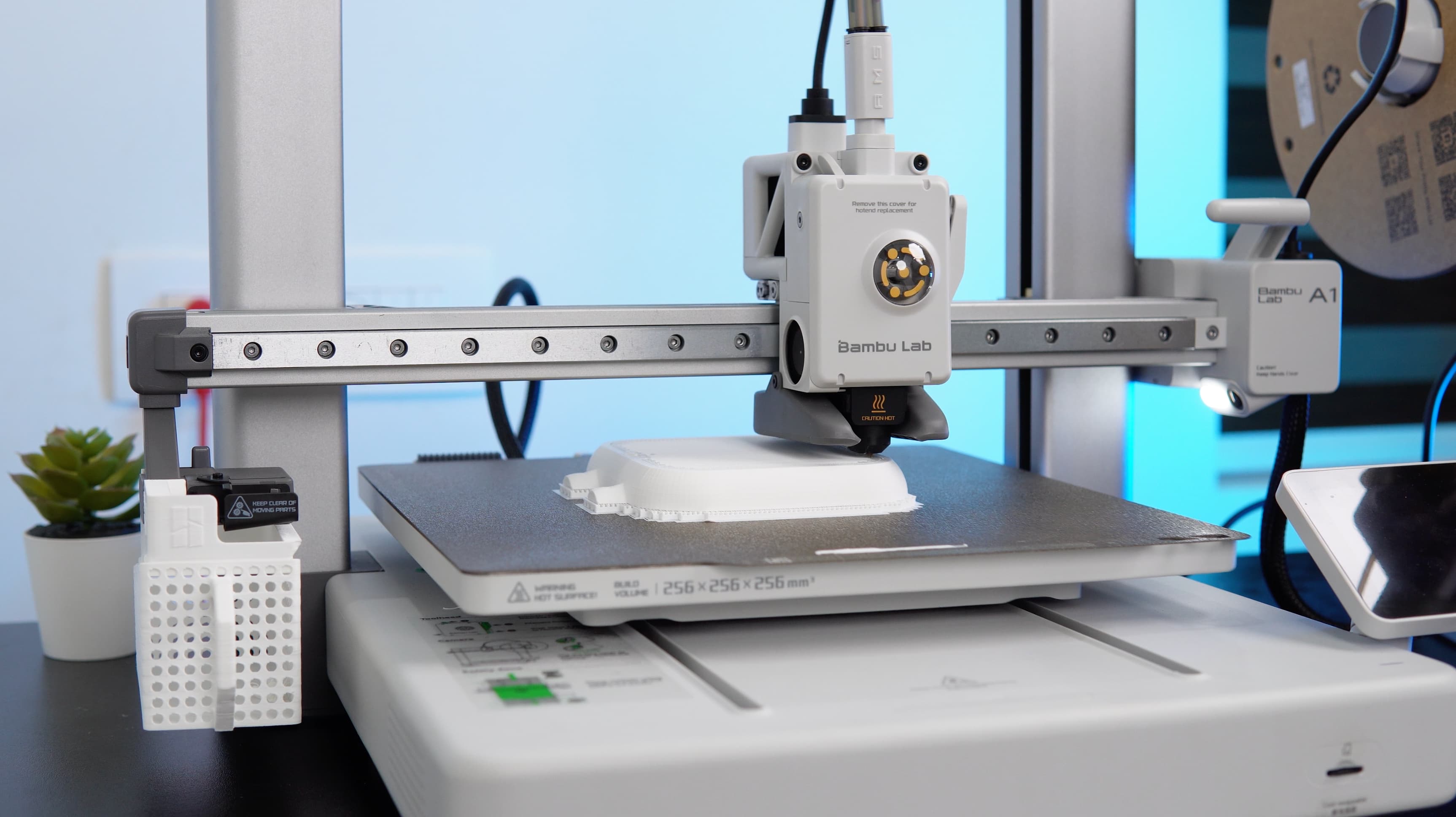
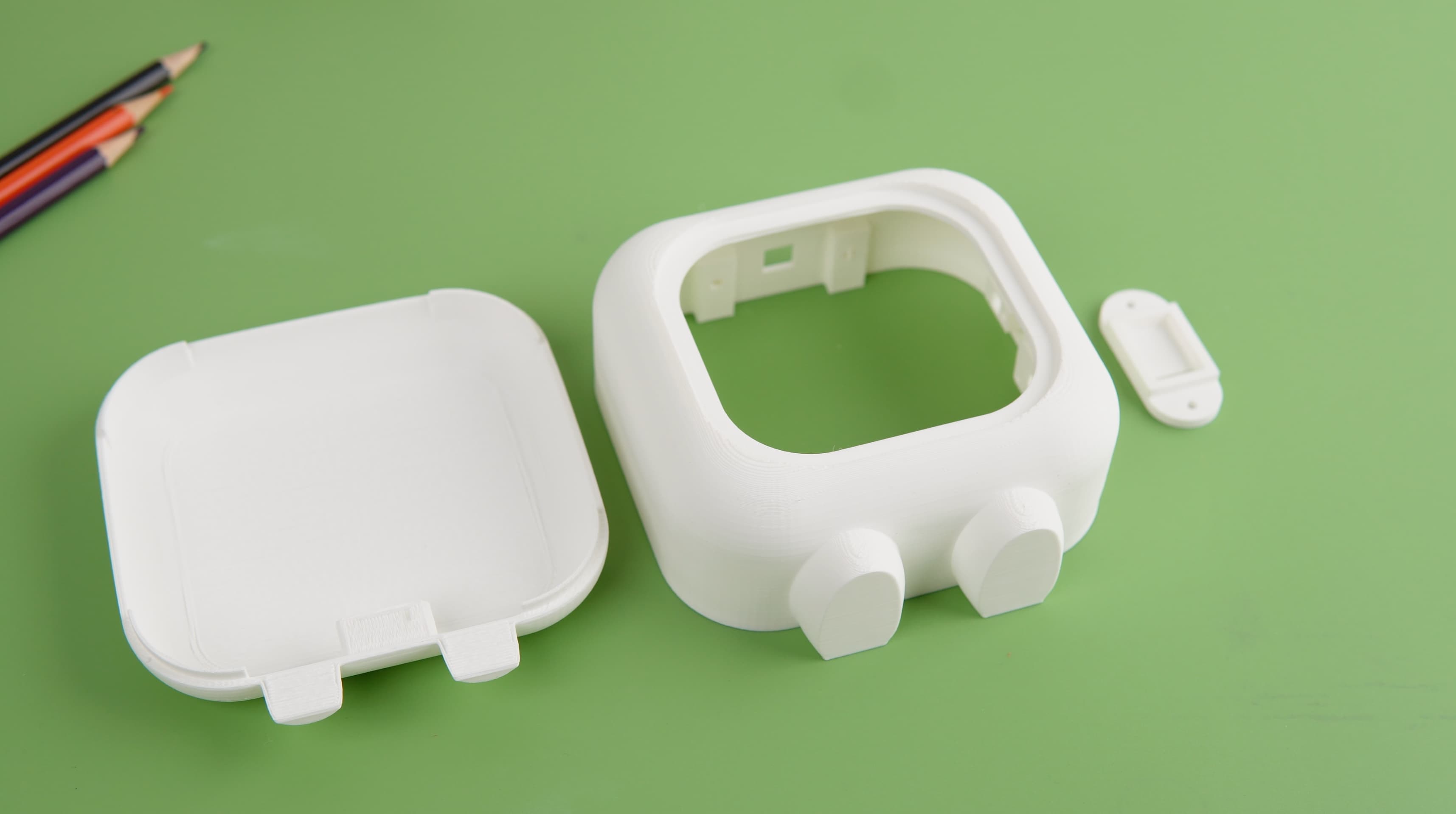
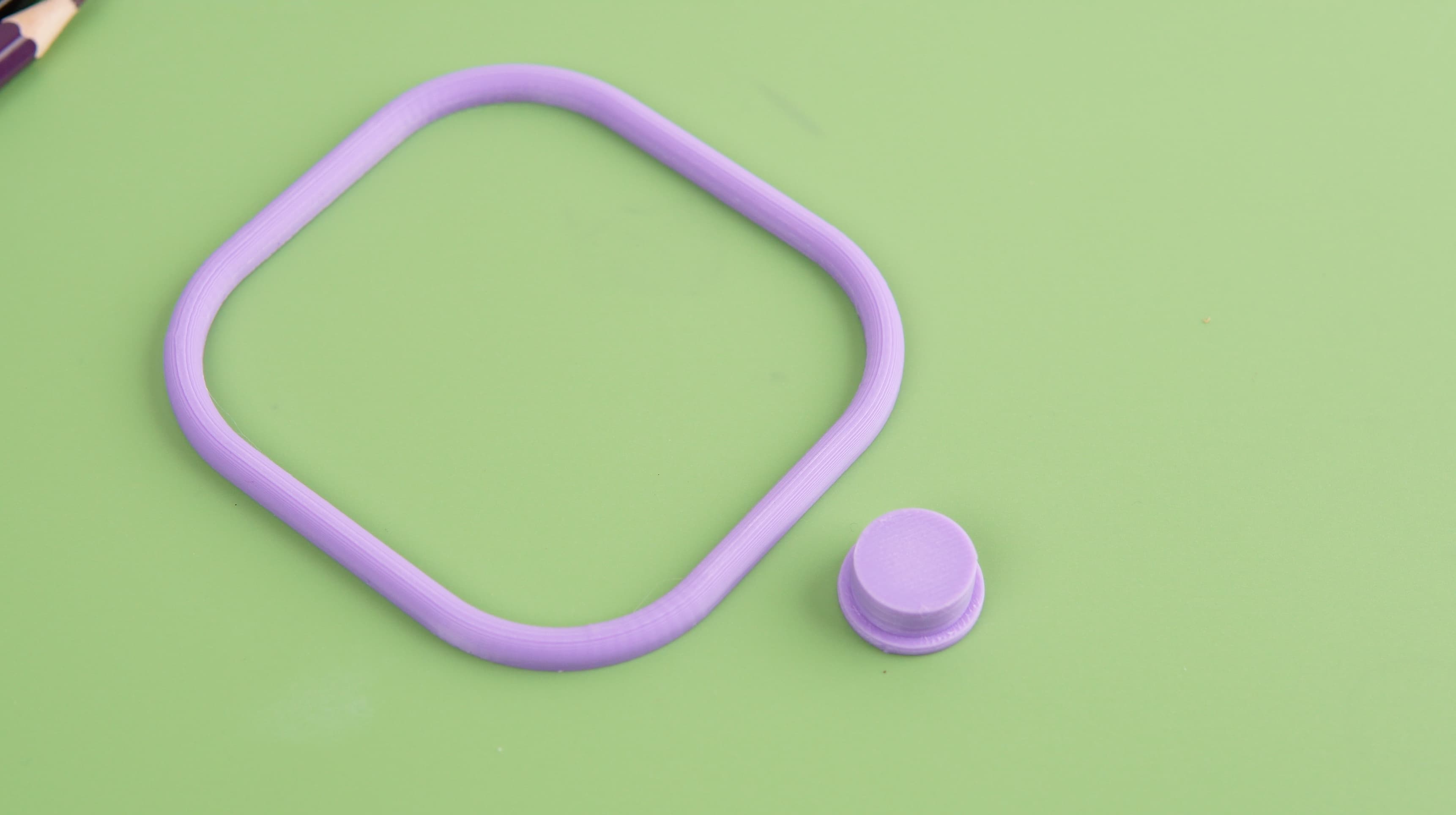



This 3D printing step was crucial in transforming the digital design into a tangible, high-quality physical product.
Find the STL Files here.
- Soldering: We began by soldering wires to all necessary components, ensuring reliable electrical connections.
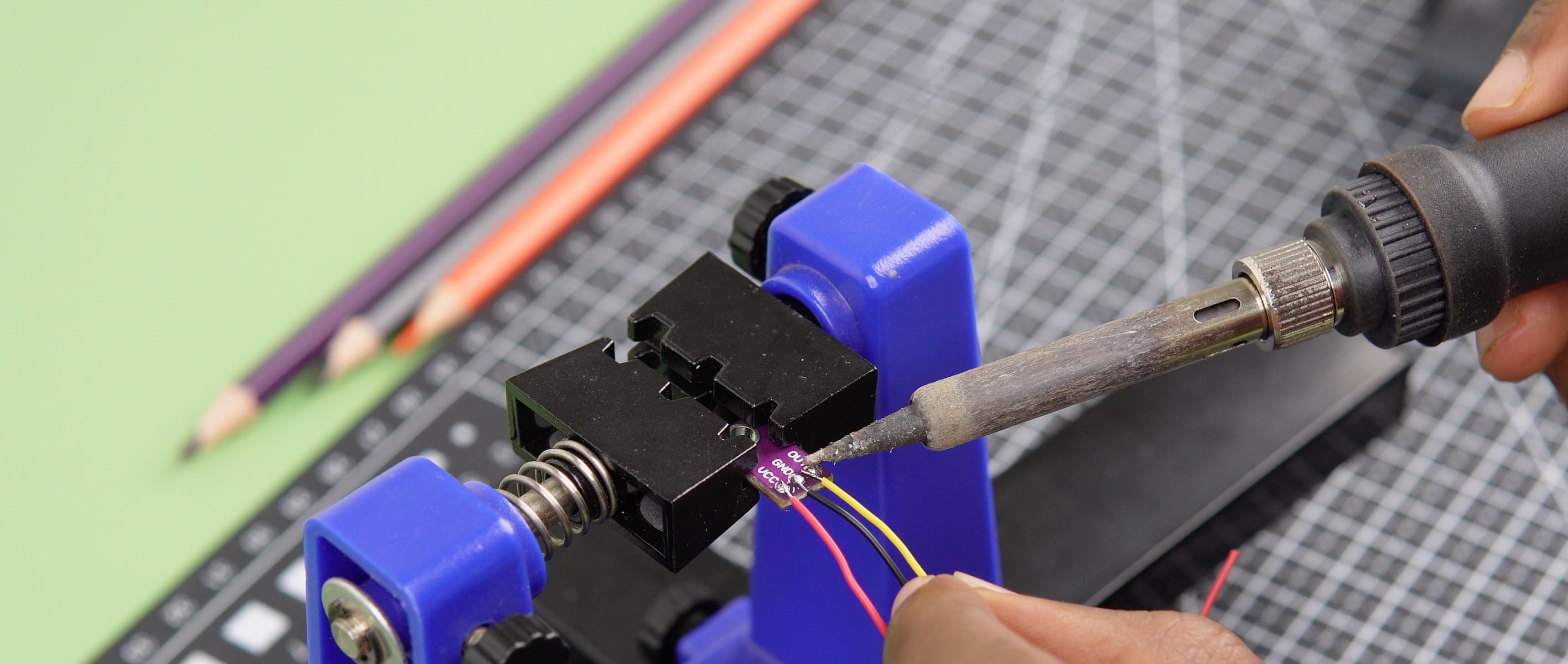
- Component Mounting: We secured the components together using tiny screws, creating a firm and stable assembly.
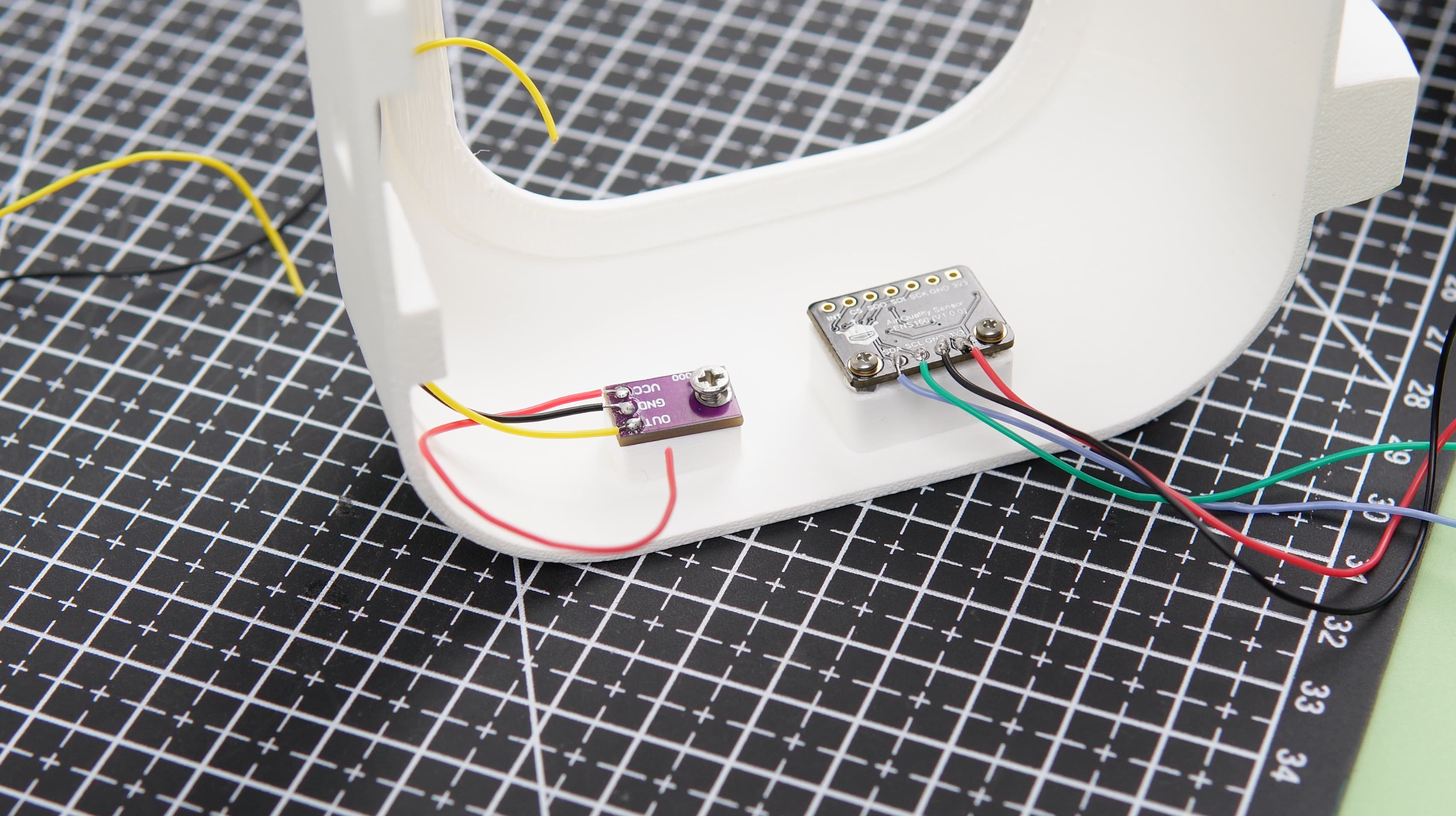
- Raspberry Pi and Display Integration: The Raspberry Pi and Waveshare display were carefully installed into the main body of the project.
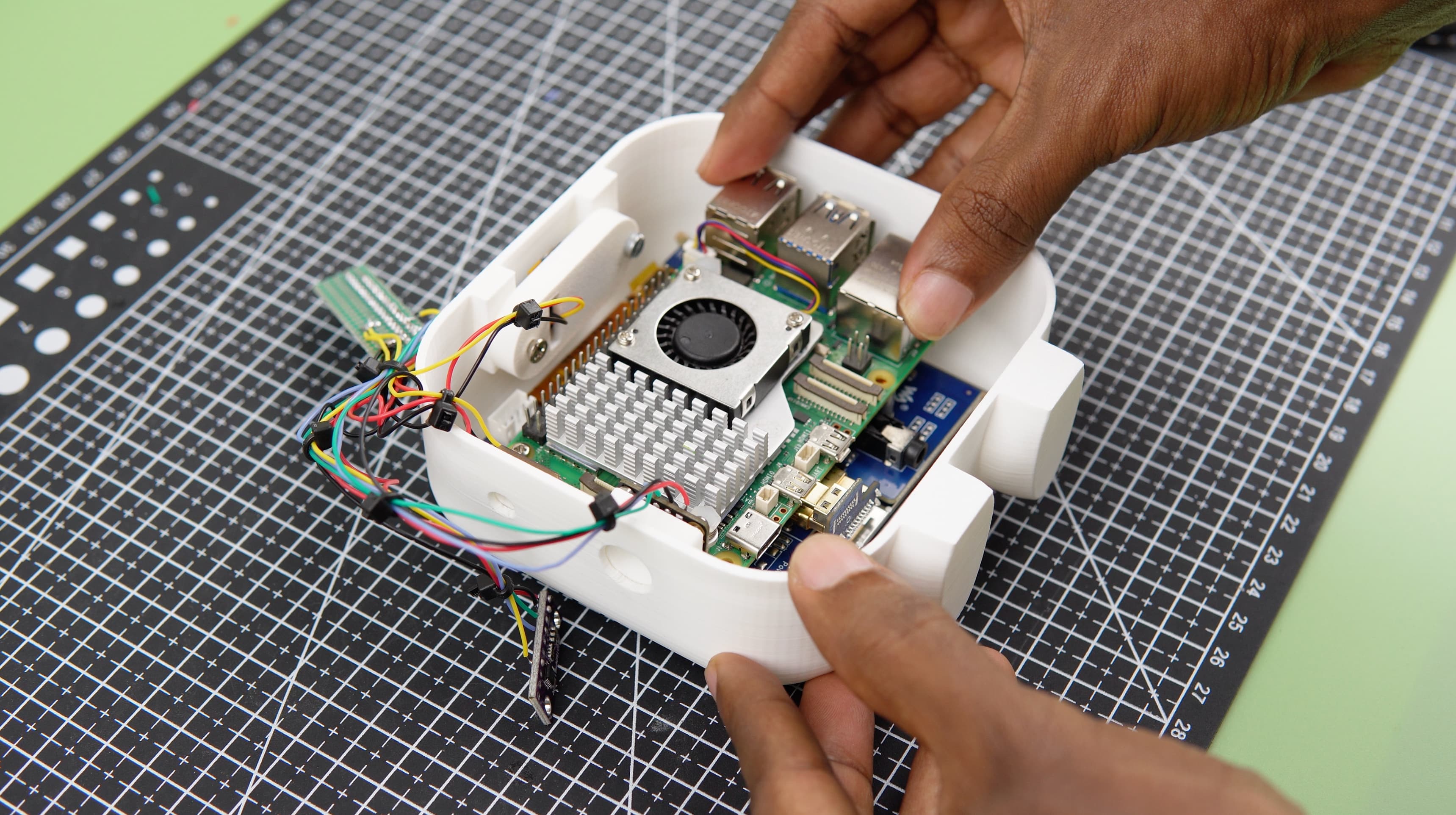
- Modular Connections: Female headers were utilized to solder connections between the components and the Raspberry Pi, facilitating modularity and ease of maintenance.
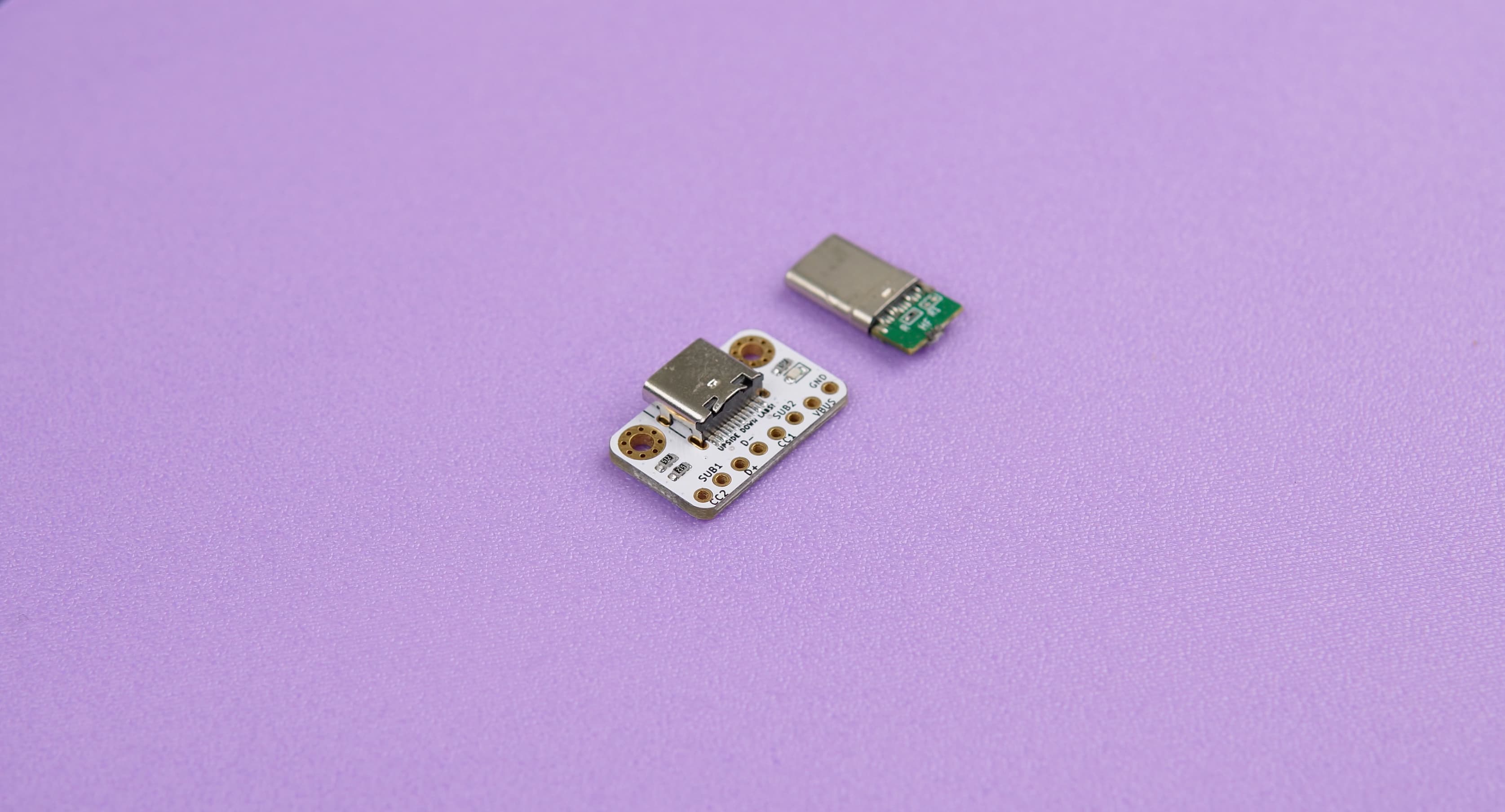
- Power Delivery: Male and female USB breakout boards were employed to efficiently power the Raspberry Pi.
- Final Assembly: The back cover was positioned and secured, completing the assembly process.
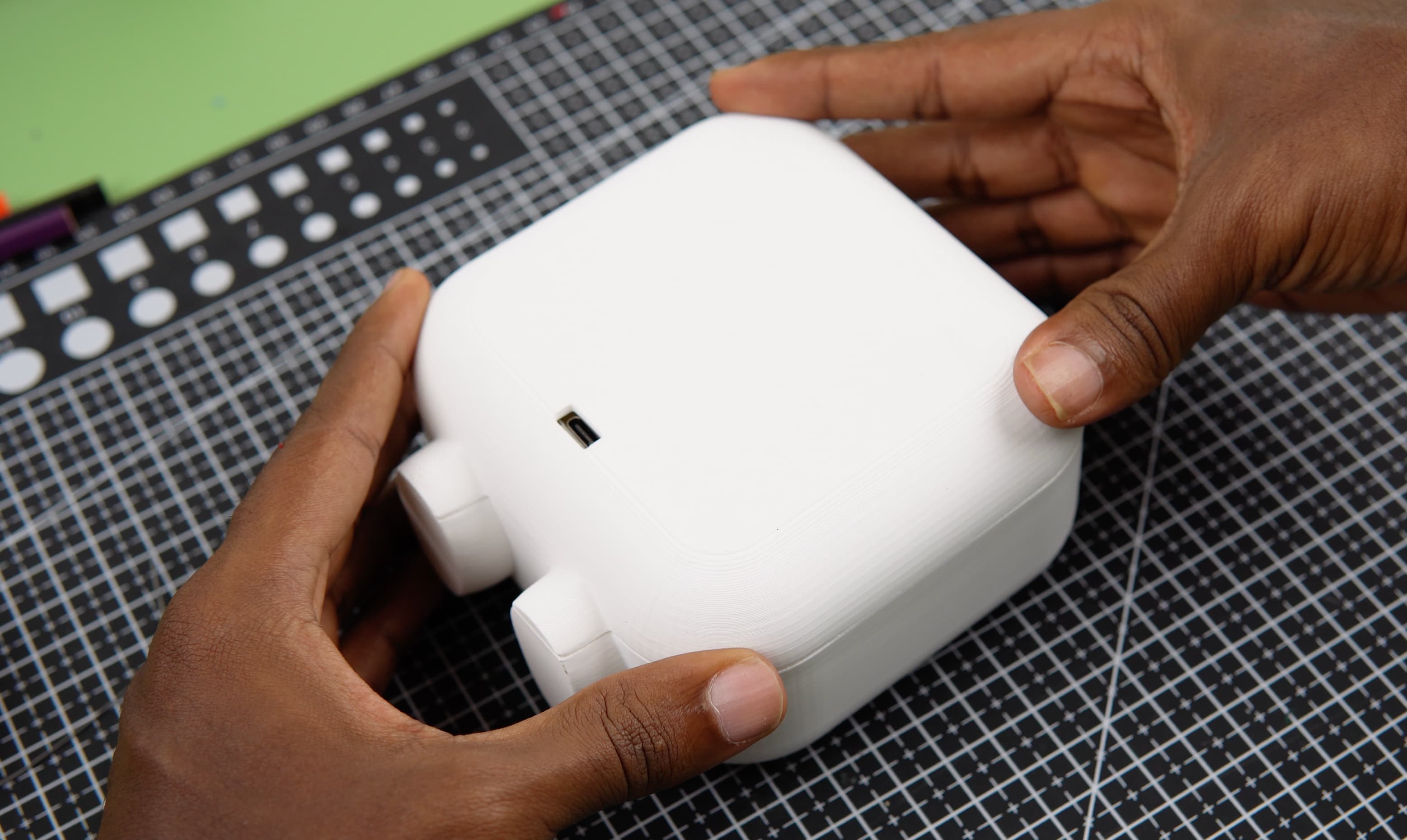

- Result: The final result is a sleek and functional Pomodoro Bot ready to enhance productivity and brighten any workspace.
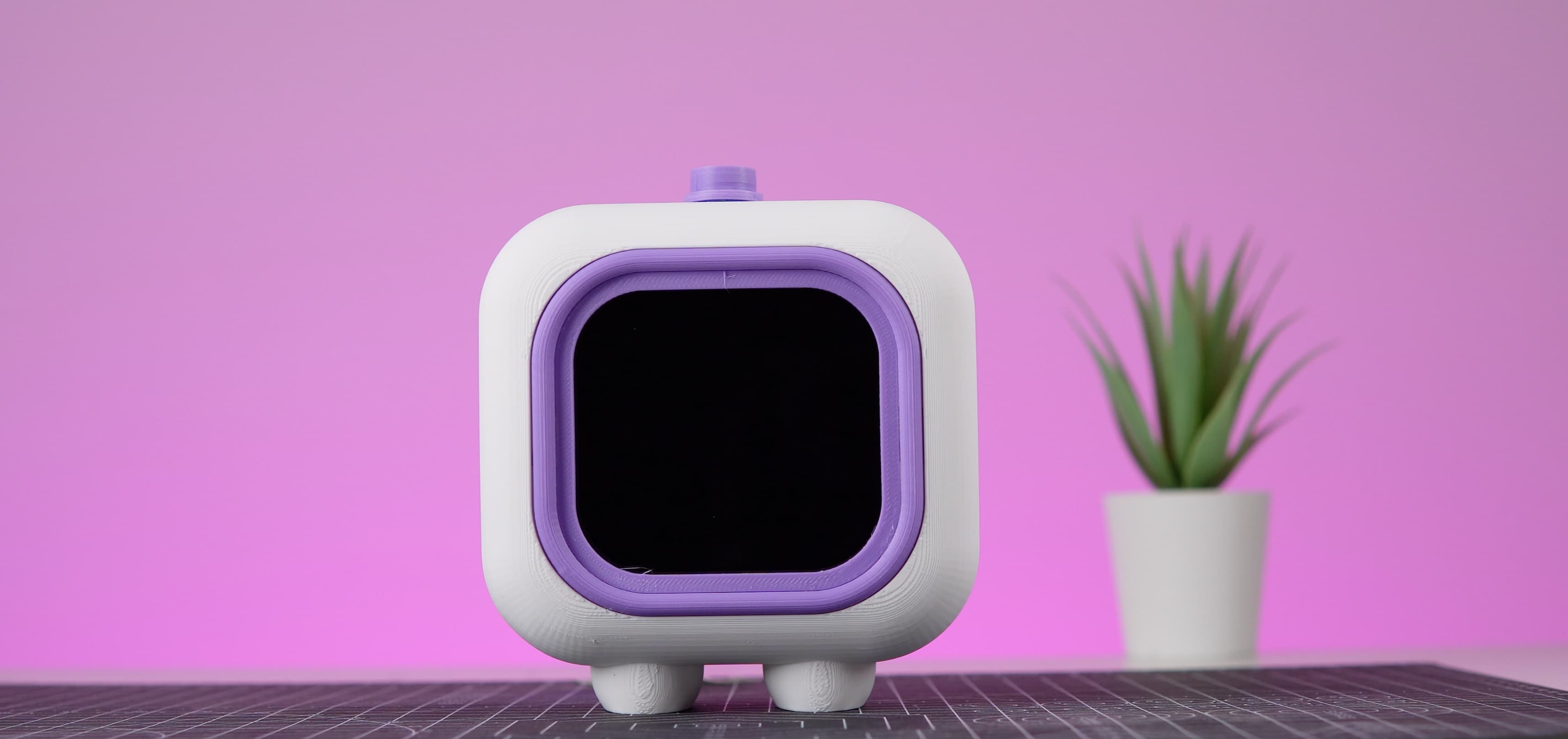

1. Power Up the Raspberry Pi
Once the assembly process is complete, power up your Raspberry Pi. You can do this by connecting the power supply to the Raspberry Pi's power jack.
2. Verify Functionality
After powering up, take a moment to verify that everything is functioning as expected. This may involve checking the Raspberry Pi's LED indicators and ensuring the Waveshare display turns on.
3. Download Source Code
The next step is to download the source code for the Pomodoro Bot application on to your Raspberry Pi. You can download the code from the following GitHub repository:
4. Edit the Source Code (main.py)
- Open the downloaded source code and navigate to the
Codedirectory. Locate the file namedmain.py. - Within
main.py, you will need to replace the following placeholders with your own values:- API Key: Locate the section where the API key is stored and replace it with your own API key.
- API Key ID: Similarly, find the section where the API Key ID is stored and replace it with your unique ID.
- Component Names (Optional): If you have used different component names during configuration, you may need to modify the corresponding names within the code.
5. Run the Pomodoro Bot Code
- Once you've made the necessary edits to
main.py, save the changes. - Back in the Configure tab in the Viam app, add a new Process.
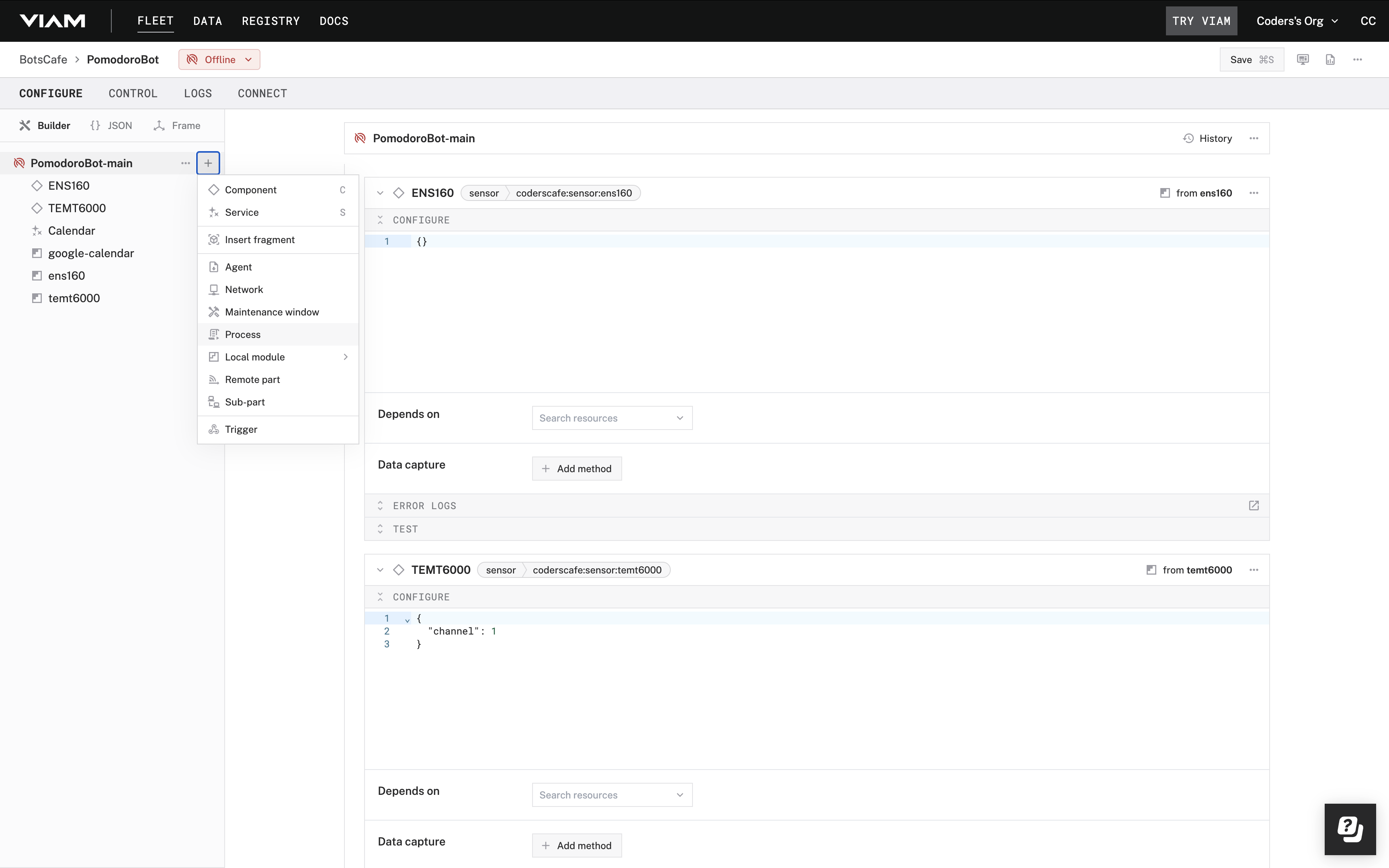
- Configure the Process by adding relevant details like Executable, Arguments and Working Directory.
- Executable: python3
- Arguments: main.py (Python script name)
- Working Directory: /home/pi/PomodoroBot/Code (Your working directory)

- Save and wait for the process to finish setup.
6. See Your Pomodoro Bot Alive!
If everything is configured correctly, the Pomodoro Bot application should launch and your Raspberry Pi will transform into a functional Pomodoro Bot, ready to help you manage your work sessions and boost your productivity.